If 2024 felt unstable for SEO, 2025 was the year things finally became clear. Not easier. Not calmer. Just harder to fake.
A lot of comfortable assumptions stopped working. Link volume lost its magic. Mass outreach became risky. AI stopped being a shortcut and started acting like a mirror that shows exactly how much expertise is really there. Search didn’t turn friendly, but it did turn more honest.
This was also the year when optimizing for algorithms stopped being enough. Search engines began behaving less like systems and more like evaluators. They compare sources, look for agreement, and reward experience that can be verified across the web. In that environment, links didn’t disappear, but their role changed. They became proof of trust rather than a ranking trick.
At the same time, search itself fragmented. Users get answers from AI summaries, forums, and communities, often without clicking anything at all. Visibility now happens in pieces, and authority is built across platforms, not just in Google rankings.
This year-in-review looks at the changes that actually mattered in 2025. Let’s talk about updates, policies, tools, and behavior shifts that reshaped SEO and link building in practice for 2026.

1. The Three Pillars Core Updates (March, June, December 2025)
What happened
In 2025, Google rolled out three core updates that all pushed in the same direction. Rankings became less about optimization techniques and more about whether content actually satisfies user intent. Sites built on thin pages, recycled topics, or link-heavy support started losing visibility. Sites with clear topical depth and consistent usefulness gained it.
What stood out was the consistency. Each update reinforced the same signals, leaving little room for tactical workarounds.
How this is confirmed
All three updates were officially confirmed via Google’s Search Status Dashboard. SEO agencies, including Grofuse, reported that this update finalized the integration of the Helpful Content system into the core algorithm.
Industry-wide traffic data showed that sites hit early in the year rarely recovered without making substantial content changes, not link adjustments.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this marked the end of using links as a fix for weak content. Backlinks stopped compensating for pages that fail to meet intent.
For link building, the role of links shifted. They no longer create authority on their own. They confirm it. Links amplify strong content, but add little value when the foundation is weak. In 2025, link building became a validation layer rather than a primary ranking lever.
2. The Helpful Content System Became Part of the Core Algorithm
What happened
In 2025, Google completed a long transition by fully folding the Helpful Content system into its core ranking logic. What used to be a separate classifier quietly became a permanent filter applied to everything. Sites were no longer evaluated page by page. They were evaluated by intent. If a site consistently produced content that existed mainly to rank, that pattern became hard to escape.
This change made “unhelpful” content a site-wide problem rather than an isolated issue.
How this is confirmed
The March 2025 Core Update was widely reported by SEO agencies as the moment when the Helpful Content system stopped operating independently. Google confirmed the update through its Search Status Dashboard, and post-update analysis showed no recovery cycles typical of past Helpful Content updates.
Sites affected earlier by Helpful Content signals continued to underperform throughout the year, even after acquiring new backlinks, unless they made significant content and positioning changes.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this removed the safety net. Publishing a few strong pages no longer offsets a large volume of low-value content. Overall usefulness became the baseline.
For link building, this raised the entry bar. Links pointing to pages on an “unhelpful” site carry limited weight, regardless of their quality. In 2025, earning links started with fixing content intent at the site level. Without that foundation, link acquisition became expensive, slow, and often ineffective.
3. The August 2025 Spam Update Cracked Down on Link Arbitrage

What happened
In late summer 2025, Google rolled out a prolonged spam update that went after a business model rather than a single tactic. Sites built primarily to host guest posts, sell links, or monetize authority through arbitrage started losing visibility at scale. Many of these sites were not technically spammy. They looked editorial, had traffic, and published regularly. What gave them away was intent. They existed mainly to pass ranking value.
This update made it clear that “looks legitimate” is no longer enough.
How this is confirmed
Google officially tracked the spam update from August 26 through September 2025, making it one of the longest spam-related rollouts in recent years. Post-update analysis across SEO communities showed widespread ranking drops among guest-post-heavy publishers and link marketplaces.
Agencies tracking site reputation abuse reported that affected domains struggled to regain visibility even after removing outbound links or reducing sponsored content.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this reduced the pool of “safe” link sources almost overnight. Many sites that passed traditional quality checks stopped carrying real value.
For link building, the update forced a shift away from volume-driven placement. Links from arbitrage-driven sites became a liability rather than an asset. In 2025, the safest links came from publishers that link selectively, publish for audiences first, and have something to lose by linking carelessly.
4. AI Overviews Became a Default Search Layer
What happened
In 2025, AI Overviews stopped feeling experimental and started behaving like a permanent layer of search. For a growing share of queries, users were shown AI-generated summaries before any traditional results. In many cases, those summaries fully answered the question, leaving organic listings as supporting context rather than the main destination.
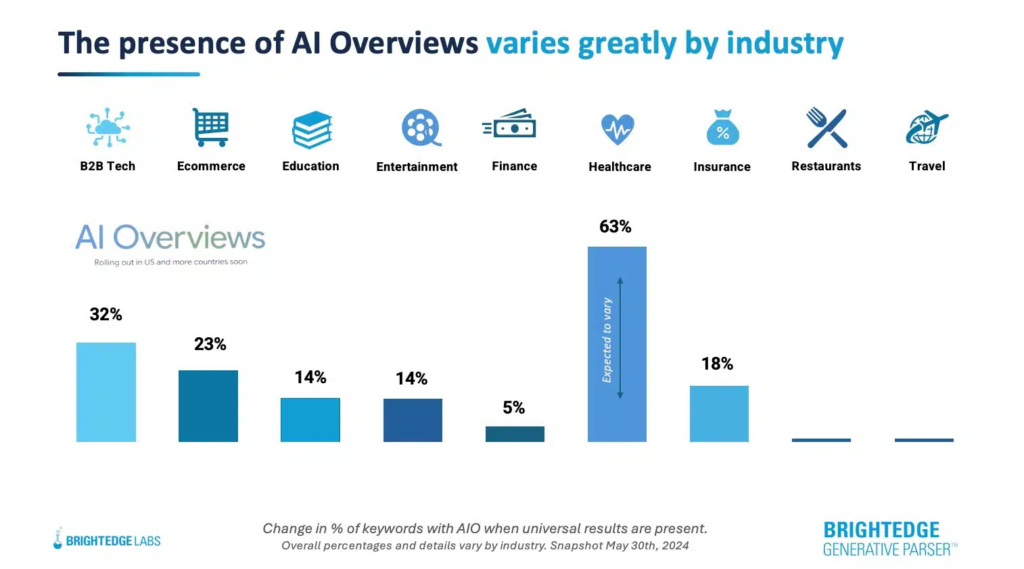
How this is confirmed
Multiple industry studies throughout 2025 tracked a steady increase in AI Overview visibility, with peaks during mid-year updates and broad international rollout across more than 200 countries. Semrush data showed AI Overviews appearing for a significant portion of informational and commercial queries, while clickstream data confirmed reduced interaction with classic blue links when AI summaries were present.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, rankings alone stopped telling the full story. Being visible inside an AI answer became just as important as ranking on page one.
For link building, this shifted the goal from passing PageRank to earning citations. Links now help establish a page as a trustworthy source that AI systems feel confident referencing. In 2025, links didn’t just support rankings. They helped decide who gets quoted when no one clicks at all.
5. Direct Citation Reward Emerged as a Ranking Signal
What happened
In 2025, search systems began clearly favoring sites that are repeatedly cited by AI models as reliable sources. Being referenced inside AI-generated answers started to correlate with stronger visibility overall, even when traditional rankings stayed flat. Authority was no longer inferred only from links pointing to a page, but from how often that page was used as a source of truth.
How this is confirmed
Throughout the year, multiple studies and SEO case analyses showed that pages frequently cited in AI Overviews and conversational search interfaces tended to maintain or improve visibility despite declining click-through rates. This pattern became especially visible after mid-year core updates, when citation frequency aligned closely with perceived authority across queries.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this introduced a new success metric: being reference-worthy, not just rank-worthy.
For link building, links now work upstream. They help position a page as a credible source that AI systems are comfortable citing. In 2025, links increasingly influenced who gets quoted, not just who ranks.
6. Google AI Mode Introduced Conversational Search
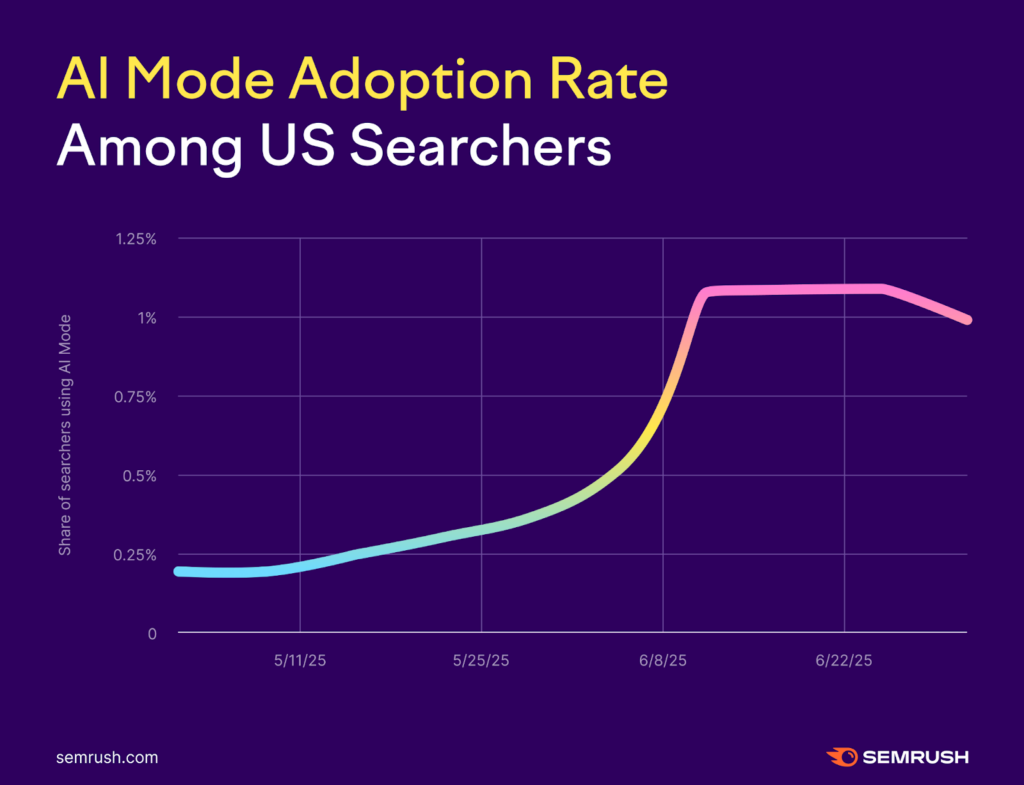
What happened
In 2025, Google introduced AI Mode as an experimental search experience that lets users interact with results conversationally. Instead of scanning a list of links, users ask follow-up questions, refine intent, and explore a topic in steps. This shifted visibility away from single pages toward sources that can support an ongoing explanation.
How this is confirmed
Google announced AI Mode at Google I/O 2025 and began limited rollout soon after. Early testing and public demos showed that AI Mode favors content broken into clear sections, definitions, and supporting references rather than long-form narrative pages.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, content needs to be modular and reference-friendly to stay visible across conversational turns.
For link building, this increased the value of links pointing to well-structured resources. In 2025, links worked best when they supported content that AI systems could easily reuse, quote, and recombine in dialogue rather than just rank once and disappear.
7. llms.txt Emerged as a New AI Crawling Standard

What happened
In mid-2025, llms.txt appeared as a new root-level file designed specifically for AI crawlers. Unlike robots.txt, which focuses on indexing and crawling, llms.txt is about interpretation. It lets site owners signal which parts of their content AI models can use, quote, or summarize, and under what conditions.
This marked a shift from managing bots to managing intelligence.
How this is confirmed
The llms.txt standard began circulating publicly in mid-2025 and was documented by multiple hosting and infrastructure providers shortly after. Early adoption was visible among tech publishers and data-heavy sites that wanted more control over how their content appears in AI-generated answers.
Industry discussions around Gemini, GPT-based tools, and other LLM crawlers increasingly referenced llms.txt as a separate layer from traditional crawl directives.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this added a new optimization surface focused on AI visibility rather than rankings.
For link building, it reinforced a key trend: links now support how content is used, not just how it ranks. In 2025, earning links to content that AI systems are allowed and encouraged to cite became more valuable than links to pages optimized only for classic search results.
8. AEO Audit Tools Entered the SEO Stack
What happened
In 2025, a new class of tools appeared with a very specific goal: measure how likely a page is to be cited by AI systems. Instead of scoring keyword usage or backlink counts, these tools evaluated structure, clarity, sourcing, and how easily content can be extracted, summarized, and referenced by answer engines. This marked a shift from optimizing pages to rank toward optimizing them to be used.
How this is confirmed
Throughout 2025, multiple SEO platforms and independent tools introduced features focused on “citation readiness” and AI visibility. Industry discussions increasingly separated classic SEO audits from AEO-focused audits, especially after the wider rollout of AI Overviews and conversational search interfaces. Case studies showed that pages scoring well in these tools were more likely to appear as cited sources in AI-generated answers, even when they did not hold top organic positions.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this added a new layer of optimization centered on clarity, structure, and trust rather than keywords alone. Pages now compete on how well they can be understood and reused by AI systems.
For link building, AEO tools changed targeting logic. Links became more valuable when they pointed to pages designed for citation, not just ranking. In 2025, the question shifted from “Can this page rank?” to “Would an AI confidently quote this page?”
9. Zero-Click Searches Became the Default Outcome
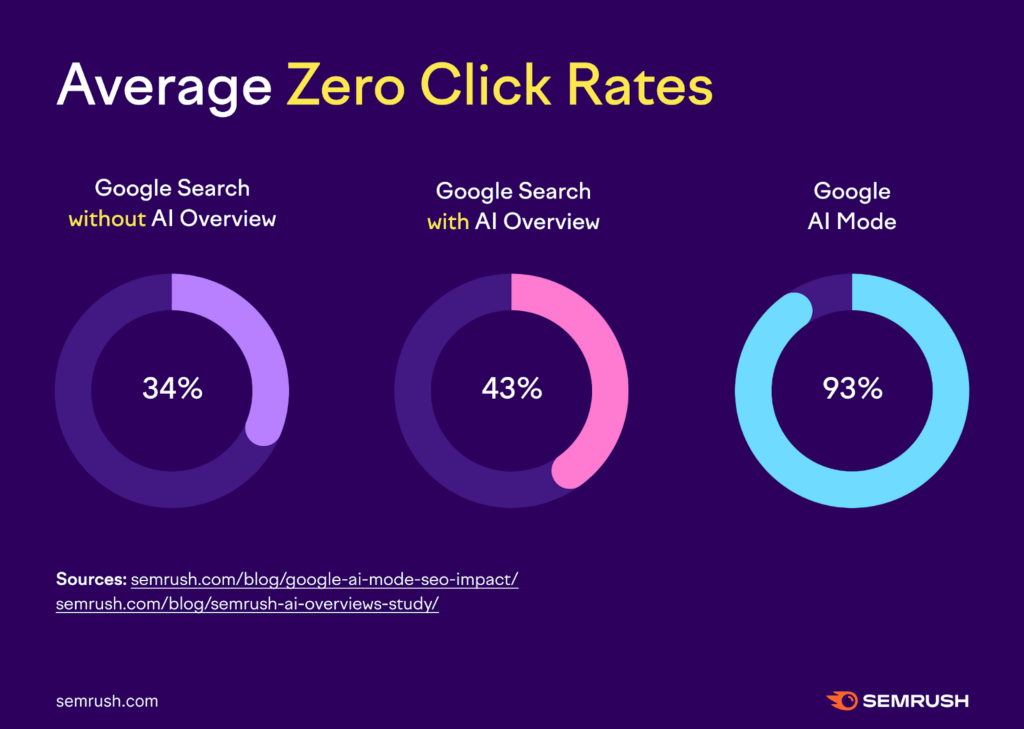
What happened
By mid-2025, getting an answer without clicking anything became normal behavior. AI Overviews, instant answers, and expanded SERP features meant users often solved their problem directly on the results page. For many informational queries, clicking through to a website became optional rather than expected.
This quietly changed what “success” in search even looks like.
How this is confirmed
Multiple studies published in 2025 showed a sharp rise in zero-click searches, with mobile queries leading the shift. Data from Similarweb and ClickVision indicated that a majority of global searches now end without a site visit, largely due to AI-generated summaries and enhanced answer modules. This trend accelerated after the mid-year core updates expanded AI Overview visibility.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, traffic stopped being the only meaningful KPI. Visibility, brand recall, and presence inside AI answers became just as important.
For link building, this reframed the purpose of links. Links now help establish authority and credibility that AI systems rely on, even when users never click through. In 2025, links increasingly worked behind the scenes, influencing who gets cited rather than who gets visited.
10. Structured Data Became a Requirement, Not an Enhancement
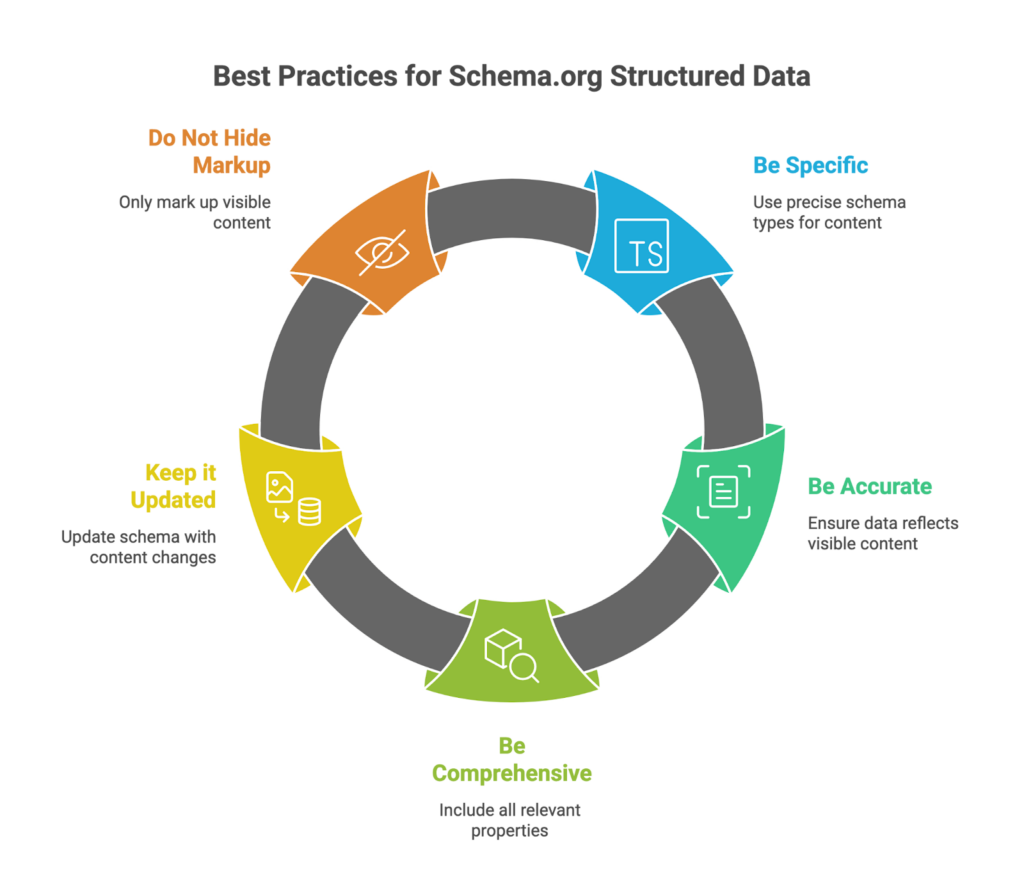
What happened
In 2025, structured data crossed an invisible line. Schema markup stopped being something that “helps” and became something that’s expected. Pages without clear, machine-readable structure were still indexed, but they were far less competitive in AI-driven search environments. When answers are generated, extracted, and recombined, structure matters as much as content itself.
How this is confirmed
Multiple 2025 industry analyses showed a strong correlation between comprehensive schema usage and citation frequency in AI Overviews and conversational search results. SEO teams tracking AI visibility reported that pages lacking structured data were significantly less likely to be referenced, even when content quality was comparable. This gap became more visible after mid-year algorithm updates expanded AI-powered features.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, technical foundations regained importance. Content that isn’t clearly structured is harder for AI systems to trust and reuse.
For link building, this changed how link value materializes. Links pointing to well-structured pages are more likely to translate into citations and visibility. In 2025, links didn’t just need strong content behind them. They needed content that machines can actually understand.
11. First-Hand Experience Became a Ranking Advantage
What happened
In 2025, the web was flooded with AI-generated summaries, and search systems responded by rewarding something very simple: proof that a human has actually done the thing they’re writing about. Pages that showed real-world photos, original data, screenshots, videos, or personal case studies started outperforming polished but generic content. Experience stopped being implied and started needing evidence.
How this is confirmed
After the March and June 2025 core updates, multiple SEO case studies showed higher engagement and retention rates on pages demonstrating first-hand experience. Industry reports noted that content with original visuals and documented processes consistently outperformed AI-synthesized articles, even when targeting the same queries. This aligned with Google’s stronger emphasis on the “Experience” component of E-E-A-T throughout the year.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this raised the bar for content creation. Explaining a topic is no longer enough if there’s no sign of real involvement.
For link building, experience became a link magnet. Pages backed by actual use, testing, or research earned links more naturally and held their value longer. In 2025, links increasingly followed proof, not polish.
12. Author Credentialing Became Central to Authority (E-E-A-T)
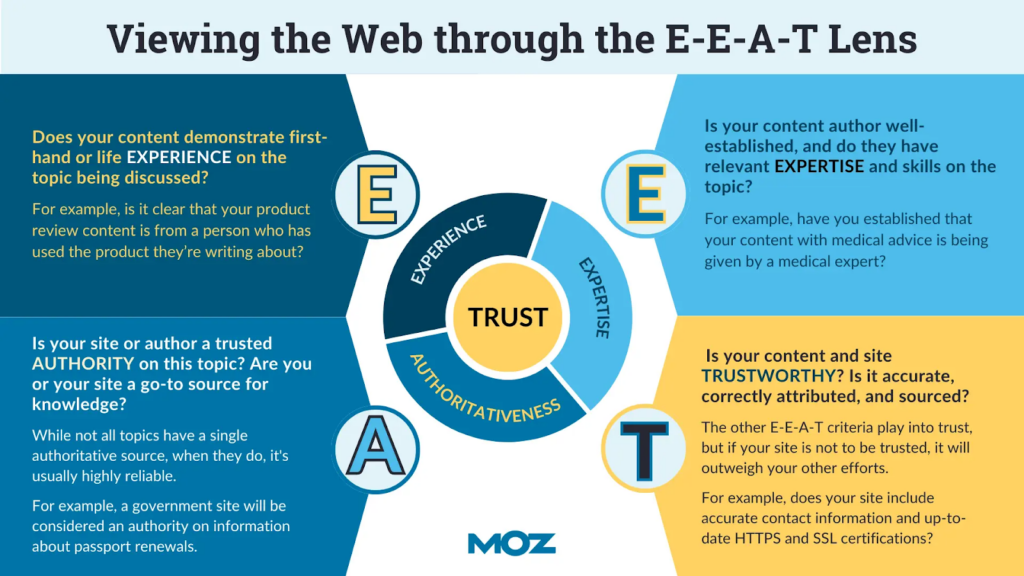
What happened
In 2025, authority stopped being purely domain-based. Who wrote the content started to matter almost as much as where it was published. Anonymous bylines, generic “editorial teams,” and placeholder author pages lost influence, while content tied to real people with visible experience gained it. Expertise needed a face, a track record, and consistency.
How this is confirmed
Following the March 2025 Core Update, multiple SEO analyses noted stronger performance for sites with clear author attribution, detailed bio pages, and externally verifiable credentials. This aligned with Google’s increased emphasis on the “Experience” component of E-E-A-T and was reinforced throughout subsequent updates. Sites that improved author transparency saw more stable recoveries than those that focused on links alone.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, authority became personal as well as technical. Content without accountable authorship struggled to compete, even on strong domains.
For link building, value shifted from domain-to-domain to author-to-author. Links connected to recognized experts carried more weight than anonymous placements. In 2025, earning trust increasingly meant earning it through people, not just pages.
13. Reddit and Quora Took Over Experience-Driven Queries
What happened
In 2025, Google leaned heavily into what it framed as “authentic human experience.” For product research, troubleshooting, and opinion-based queries, forum threads started outranking polished editorial content. Real conversations, disagreements, and firsthand stories became more visible than curated marketing pages.
This wasn’t a temporary experiment. It stuck.
How this is confirmed
Multiple late-2025 studies showed “Discussions & Forums” blocks appearing in a large share of commercial and review-type queries. Google’s own guidance increasingly referenced authentic experience as a quality signal. Visibility gains were especially clear for platforms like Reddit and Quora, which consistently appeared above traditional affiliate and blog content.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, optimization expanded beyond owned sites. Reputation, participation, and visibility inside communities started influencing search performance outside them.
For link building, mentions and contextual references became more important than clean dofollow placements. In 2025, being discussed by real users often carried more authority than being linked from another “SEO-friendly” page.
14. Generic “Best Of” Listicles Lost Their Influence
What happened
In 2025, one of the most overused SEO formats finally cracked. Generic “Best [Product]” and “Top Tools” listicles, especially those built without real testing or experience, started losing visibility across competitive queries. Search systems became much better at spotting recycled comparisons, affiliate-first rankings, and content that exists mainly to funnel clicks rather than inform decisions.
How this is confirmed
Industry reports throughout 2025 highlighted sharp traffic drops across large affiliate and comparison sites that relied on templated reviews. The Digital Bloom 2025 Organic Traffic report described this as part of a broader “decoupling,” where generic informational and comparison content was replaced by AI summaries or more experience-driven sources. Recovery was rare without adding original testing, data, or clear proof of use.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, this raised the bar for commercial content. Simply aggregating features or prices is no longer competitive without first-hand insight.
For link building, it removed a major source of easy links. Links from generic comparison pages lost much of their value unless backed by real testing and credibility. In 2025, links from review content started carrying weight only when the review itself was something a human would actually trust.
15. Search Fragmentation Made “Everywhere Optimization” Necessary
What happened
In 2025, search stopped meaning one place. Users increasingly discovered information through AI tools, forums, and social platforms, often without ever opening Google. Asking a question in an AI chat, scanning a Reddit thread, or watching a short explainer video became part of the same decision journey. Traditional search was still important, but no longer dominant on its own.
How this is confirmed
Throughout 2025, industry reports documented rising usage of tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity for research and discovery. At the same time, Google traffic growth flattened in several informational niches, while referral and brand-driven traffic diversified across platforms. This shift was widely discussed under the umbrella of Answer Engine Optimization.
How this impacts SEO and link building
For SEO, optimization expanded beyond Google rankings. Being discoverable now means being present wherever questions are asked.
For link building, this broadened the definition of authority. Mentions, citations, and references across multiple platforms started reinforcing each other. In 2025, links mattered most when they supported visibility across the entire search ecosystem, not just one engine.
Conclusion

2025 didn’t quietly tweak SEO. It rewrote its rules in plain sight. Link building didn’t disappear, but it lost its ability to work in isolation. Authority now comes from being useful, recognizable, and consistently referenced across intelligent systems, communities, and platforms. Links still matter, but only when they support real expertise, real experience, and content that deserves to be used, not just ranked. Going into 2026, the direction is hard to argue with. Search rewards credibility first and optimization second, and there’s no practical way back to how things used to work.






