When it comes to SEO today, many experts agree that content is king. Your content is what your potential and active customers see, it is how they judge whether your services or products are worth spending their money on. Content is your strongest online marketing instrument and for this instrument to be efficient, you need to create a solid, data-driven strategy. In this article, we will talk about creating a SEO content strategy in detail, offer actionable tips, analyze various approaches to the process and walk you through all steps of it.
What is SEO Content Strategy and Why It Is Important
Terminology:
SEO Content Strategy refers to the strategy of creating content with the goal of driving search engine traffic to your website. Seo Content is information-rich content that targets specific keywords and provides a great user experience. The types of SEO content can include blog posts, articles, white papers, case studies, videos, infographics, and more. This content is specifically tailored to engage audiences and encourage sharing, which improves search visibility.
SEO content is structured and created in a specific way to make search engines pick your resource over others that offer content in the same niche and show it to users who look up information in your niche on the internet. The algorithms that search engines, specifically, Google, use to determine which content better responds to a particular user query are very complex and estimates dozens of factors. These factors range from uniqueness, engagement and user experience to technical qualities, accessibility and trustworthiness, to name but a few. The main goal of SEO content strategy is to plan your content so that it takes into account all these factors and provides the best possible response to search queries that your potential customers may have.
There are several important reasons why you need a carefully crafted strategy to create this kind of content:
1. Structured approach
A structured strategy helps you to organize creation of content around topics that matter most to your audience. It also helps you to effectively distribute your resources on the content creation timeline.
Example:
If you sell children’s toys online, your content strategy will take into account the holiday season, focusing your content efforts for a particular time of year. During the holiday season of 2015, Sainsbury, a high-end department store, published a cartoon, Mog’s Christmas Calamity to promote their charity campaign which includes a tie-in children’s book sold to benefit Save the Children. Even though officially, the costs to produce the cartoon were never made public, high-quality animated features like this are a very big investment in terms of production cost and marketing. The campaign was a huge success in terms of both viewer sentiment and commercial impact, skyrocketing Sainsbury’s visibility and brand name worldwide. It has over 42 million views on Youtube and is often referred to as one of the most beloved Christmas commercials, resurfacing each holiday season for almost 10 years now.
2. Topic and Keyword selection
Through a systematic strategy, you can identify and target keywords that have the right blend of search volume, relevance, and competitiveness. Since this process is continuous, making it a part of strategy helps you to keep your keywords relevant, and avoid unnecessarily expensive keywords. Your aim is not to just drive traffic, but the right kind of traffic that converts to leads and purchases.
3. Long-Term results
SEO is a continuous process and its results are usually long-term. A well-planned content strategy helps you to build a strong foundation for all of your SEO activities and work for steady increase in visibility, rankings, customer loyalty and following over time.
4. Assessment and Adaptation
With a clear content strategy, you can set clear benchmarks for success, gather data and feedback, analyze what works, what doesn’t and why. This allows you to make well-informed alterations to your content, honing it for better impact and audience reception and improving ROI from content efforts.
Steps to Create an Effective SEO Content Strategy
Step 1: Conduct a Site Audit
Your first step would be to assess what you already have. A site audit can help you to understand your website’s overall health and performance in SERP. Such analysis done in a comprehensive way, can help you uncover layers of content, define your well-performing ideas and scale them as well as blank spots.
Evaluating Existing Content for SEO Value
SEO value of your content is how well it aligns with existing best practices for SEO and how well it performs in terms of driving traffic and making conversions. Your goal here is to define well-performing content and understand what makes it such, and to improve under-performing content.
Things to do:
- Use Analytic Tools: Google Analytics and Google Search Console provide insights into how your content is performing in terms of traffic, engagement, and conversion rates.
Example:
You can run your website through Google Analytics for a Behavior Report. This report shows metrics like Pageviews, Unique Pageviews, Average Time on Page, and Bounce Rate for individual pages. For example, if you have a 5-7 minute long-read with an average time on page less than 15 seconds and a high bounce rate, it means that something in this article puts off your users right away. It could be bulky language, poor structuring, load speed or even something that you state in the very beginning.
- Check keyword rankings: Identify which keywords your content is currently ranking for and whether these rankings actually contribute to your traffic and SEO goals.
- Assess Content Quality and Relevance: you can use tools like Grammarly to check your texts for readability, grammar, uniqueness, language quality. Good SEO content should adhere to SEO best practices, including the use of relevant keywords, meta tags, and linking structures. You can also conduct subject matter expert reviews to evaluate the actual usefulness and relevance of our content.
Identify and Analyze Content Gaps
You will have to use keyword research tools to find various potential queries your target audience is searching for but you haven’t yet addressed. It’s always good to carry out this type of analysis simultaneously with competitor research. Focus on those of your competitors who score higher in rankings for particular keywords and you can find all of your blank spots.
Content gaps can have a serious impact on your SEO, so once you identify them. There are several ways to identify and analyze Content Gaps:
- Collect Feedback from Users: you can do it on social media or through service, technical support or customer care communication, any direct and indirect interaction will work.
- Comparison with Competitors: can be done through visual analysis of competitor websites to see what they have that you don’t. You can also use Moz, Ahrefs or Semrush to do an automated analysis.
- Keyword research: keyword research tools can help pinpoint keywords that your potential customers are using to search for goods or services like yours but which you haven’t optimized for yet.
Step 2: Research Keywords
Now that you have thoroughly nitpicked your website and know all of your blank spots and areas of improvement that can benefit from content addition, you can start researching keywords. If explained in simple words, keyword research is finding all possible phrases and word combinations that your potential customers use to search for products or services like yours on Google. It may seem obvious at first glance, but it’s far more complicated in fact.
Your biggest problem is this: straightforward, simple, precise keywords are expensive, and optimizing just for them is difficult and pricey.
Terminology:
Keyword Difficulty is a metric that shows how dense the SEO competition for this or that keyword is and how hard it is to try and rank for it.
How to Find High-Value Keywords
As you can see from above, high-value keywords are those that would be highly relevant to what you offer, but at the same time, will have lower difficulty.
You can use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs or Semrush Keyword magic tool to research your keywords. In the example below, we are using Backlinko’s free keyword difficulty tool.
If you are marketing pet care and grooming services, optimizing for ‘pet grooming’ puts you in the highest level of difficulty, because the keyword ‘pet grooming’ has a difficulty of 69. Which means, unless you already are a very high-authority website, well-established in your niche, you simply won’t be able to rank well for it.
However, if you try to narrow down the search, you’ll see how the difficulty decreases the more specific your query is: grooming for cats has the difficulty of 58, so, you’ll still need a very strong on-page SEO and backlink profile to link for it. If we make it ‘grooming for longhair cats, the difficulty drops down to 35. Difficult, but marketable.
Now, if you make it ‘grooming for maincoon near me’, we get a difficulty of 16. If you make a list of similar keywords with popular cat and dog breeds that often require grooming, the chances that you hit your audience are very high.
Of course, difficulty and relevance are not the only qualities a high-value keyword has. You need your keyword pool to include a broad range of keywords, so do start broad and narrow down. Understanding that you won’t be able to rank on certain keywords, prioritize those that are more specific. Another important metric is the search volume. If a keyword is highly relevant, low difficulty, but has close-to-zero search volume, it will not drive traffic.
Long-Tail Keywords vs Short-Tail Keywords
It is important to balance both long-tail and short-tail keywords in your keyword pool. Long-tail keywords are queries that are more specific, provide more details and are used when your potential customer wants to narrow down the search from the start.
Example: if you’re selling jewelry, your long-tail keywords would be ‘cheap diamond white gold engagement rings size 16’ or ‘hello kitty gold earrings for girls”. As you can see, narrowing down can be adding brand names, specific attributes and audience to a generic name of a product or a service.
Short-tail keywords in this case would be those said generic names of products and services. They usually have a lot of competition and attract people who are at various stages of their buying cycle. This means, they may only be looking out for options, researching information on the topic and aren’t necessarily ready to buy something.
Here are some key qualities of both long-tail and short-tail keywords:
| Long-Tail Keywords | Short-Tail Keywords |
| Longer and more specificLess difficultHigher conversion due to precision | short, genericMore difficultBigger search volume |
A good keyword profile usually combines both, because you need both, to drive general traffic and potential buyers to your site to make it work.
Alignment with Search Intent
One of the more important qualities of a high-value keyword is how well it aligns with your potential customers’ search intent. On the one hand, audiences that may have importance aren’t always people that want to buy something. On the other hand, their search queries may not always be directly connected with what they are looking for: people use different wording and logic.
Search intent can generally be categorized into five types:
- Informational: user just wants information. Keywords for this type of intent can start with ‘how to’, include the words ‘guide’, ‘information’, ‘stats’, etc.
- Navigational: wants to fine a specific website or app (e.g., “YouTube”).
- Transactional: user wants to buy something or is looking up prices (e.g., “buy black Nike shoes online”).
- Commercial Investigation:user wants to compare products or services (e.g., “best DSLR cameras 2023”).
- Local: user is looking up products and services near them. Keywords for such services can include ‘near me’ or names of your particular areas, such as counties, city districts, streets, etc.
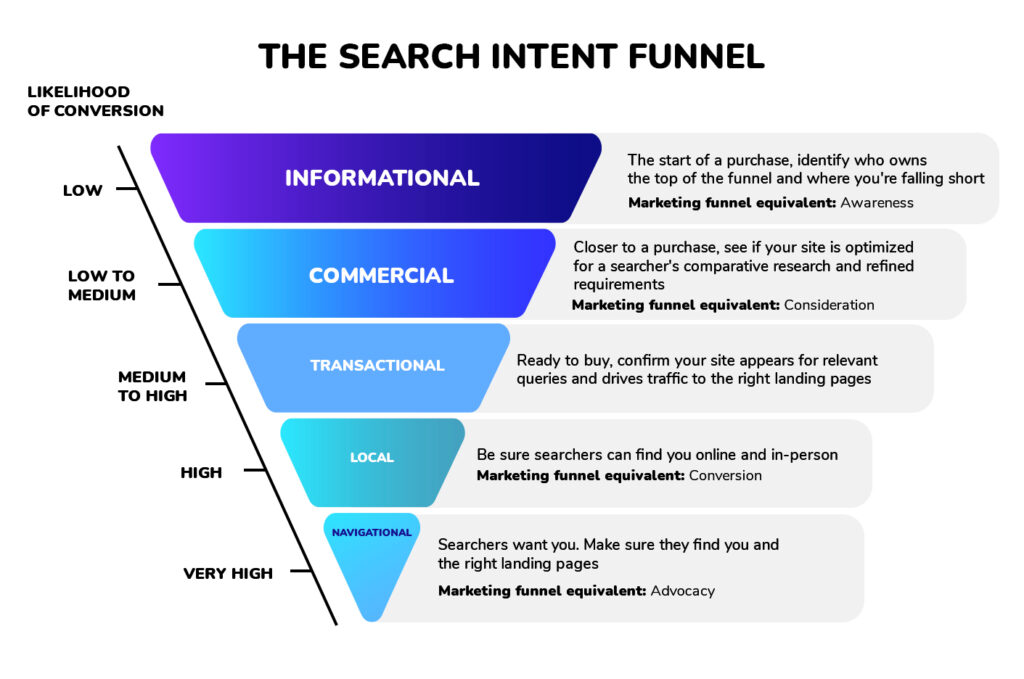
Now that you have made this research, you should have a keyword list with several metrics to each. Sorting the keywords by those metrics will help you define the most promising variants and optimize for them.
Step 3: Create a List of Topics
The next is to group these keywords into logical topics. This process is meant to help you plan your content topicwise and better align it with your business goals.
Grouping Keywords into Topics:
Take your keyword list and mark each keyword as belonging to a certain specific topic. You can even introduce a tier topic system, if you unite several highly-specific topic into more high-level topic buckets.
Example:
If your keywords include “breakfast recipes with eggs,” “breakfast smoothies,” and “quick breakfast options for school,” you could create a broader topic titled Breakfast Ideas.”
Prioritizing Topics
The metrics you’ve put down for your keywords, such as search volume, difficulty, relevance, competition should help you to create a very clear priority list. Give the best priority to lower difficulty keywords that have a relatively decent search volume, very high relevance and potentially aren’t yet covered ad nauseam by competitors.
Balancing Act:
It’s crucial to balance topics with high search volume against those that are highly specific to your business even if they have lower search volumes, as these can often convert better.
Step 4: Analyze Your Competitors
If someone’s already doing something in your niche that works, it’s worth your while taking a look. The same, it’s definitely worth your while taking a look at someone who is doing it wrong to avoid their mistakes. It’s time for competitor analysis.
Tips to look for in your competitors:
- What semantics they are using in their content and topics
- Content structure, especially for high-ranking pieces
- Check what your competitor is doing if they rank higher than you for your high-priority keywords
Assess Competitor Content and Keywords
Look at the type of content they produce, such as videos, blog posts, infographics, it’s frequency and quantity. Note what kind of topics they cover, their depth and specifics, their stats and user engagement.
Example:
If your competitor ranks highly for “Korean beauty products in Baltimore” examine their page content, structure, backlink profile and keywords to understand where their success comes from.
Content Gaps and Opportunities
You’re looking for topics that your competitors haven’t covered yet. Chances are, there are very few such topics. In this case, you need to understand whether you can add a unique twist to a beat-up topic:
- Unique POV:, personal experiences, professional commentary, expert takes, a new angle of serving the new information
- New Format: Audiences love new takes on old things. See if you can recreate the content your competitors have already covered, using a new venue. A video instead of texts. A hands-on experience instead of a generic lecture, etc.
Step 5: Plan and Develop Your Content
If you went this far, you already know what you will be writing, blogging, vidding about. There is plenty of information about how to plan and create your content, generate ideas and select content types. Let’s focus on what makes this content SEO content and how you need to incorporate this into your strategy before you start out.
Your content needs to adhere to Google’s E-E-A-T and YMYL algorithms
E-E-A-T and YMYL are principles according to which Google evaluates your content. E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. As such, in any piece of content Google looks for:
- Experience: proof that content creator has real hands-on experience in the topic
- Expertise: the depth of knowledge content creator demonstrates. This one is especially important if you talk about skills and technical understanding
- Authoritativeness: content creator proves that as a source of information they are credible and recognized by other experts in the field
- Trustworthiness: relates to how accurate your content is and how secure the usage of your website is
YMYL stands for “Your Money or Your Life. In relation to SEO, the term is coined by Google to describe a pool of topics that are vital for a person: health, financial stability, safety, major life decisions, childcare, happiness. Pages with such content are subject to higher scrutiny and standards because they make a lot of impact.
Your content needs to align with user search intent
In accordance with the types of intent we have discussed above, each piece of content you create needs to be aligned with a particular type. Even if your ultimate aim is to sell, it is much better for SEO if you combine content with various intent orientations. Thus, your informational content doesn’t need to promote your product too overtly, while transactional content should, on the contrary, facilitate a purchase.
Step 6: Optimize Content for SEO
Optimizing content for SEO deserves a series of articles. It is a science and even an art of creating unique and catchy titles, meta descriptions and headers. It also involves distributing your keywords in a natural, non-forced way. It means that your content should be relevantly interlinked. These are the basics. But as Google’s SERP calculation algorithms get more sophisticated, so do optimization strategies. For instance you can also optimize for Google Snippets or Google Discover.
Google Discover optimization is different from regular SEO, because it is a personalized content feed that is based on searches and preferences of a particular user, that get recorded by Google. Even though Google Discover guidelines state that no special optimization is needed, there are still ways to increase your chances of being selected for Google Discover. Your SEO efforts in this case should focus on content quality, relevance and user behaviors.
Here are specific best practices that help you get on Google Discover:
- Focus on evergreen content: convent that stays relevant even after a long period of time
Example: content that capitalizes on popular memes and trends has a good chance of becoming viral, but it is the opposite of evergreen: it has the shortest popularity lifespan.
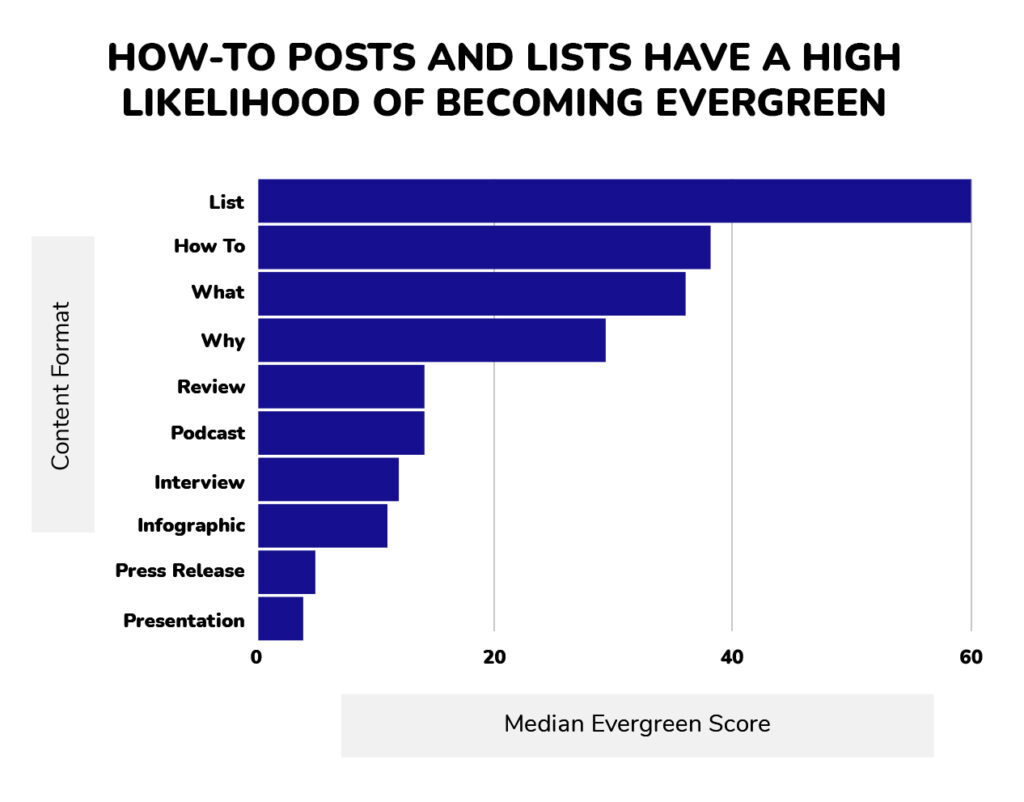
- Optimize for increasing engagement signals: likes, interactions, clicks are all signals to Google. You need to make your content visually appealing and encourages user response.
- Optimize visuals: use HQ pictures and photographs, infographics, don’t forget about proper schema markup (such as og:image or structured data)
- Mobile-friendly: Over 50% of searches today are done on a mobile device, so make sure your content looks good on a phone screen.
- Comply E-E-A-T and YMYL principles
Step 7: Organize a Content Calendar
Now that you have tackled the content itself, the situation that you want to avoid the most is when you have a good bow, but it’s in the castle. The SEO success of your content largely depends on whether you publish it at a relevant time and whether your timeline distributes types of content well. Having a content calendar is vital not for this reason alone. It also allows you to start preparing content in advance and avoiding time pressure.
Here are a few key steps to create a workable, realistic calendar:
- Define your content objectives
They have to be realistic, achievable and consider external factors, such as change of seasons. Common goals can include: traffic increase, improve brand awareness, user engagement, and drive sales.
- Choose your Tools
Spreadsheet tools such as MS Excel and Google Sheets are traditional instruments for content calendars, as they allow the necessary flexibility. They are specifically good for starting out. As your content strategy develops, you can switch to project management tools, such as Jira, where you can create a unified timeline as well as a kanban board and separate task tickets.
- Set Key Dates
Mark certain milestones and specifically important dates. For example, if your business has a seasonal nature.
- Populate the Calendar considering Content Types
Plan different types of content—blogs, social media posts, videos, newsletters—according to what works best for each platform and audience segment. Balance evergreen content with timely posts to keep your feed fresh and relevant.
- Assign Tasks
Select an assignee from your team for each particular task and set a realistic deadline for it. If you are using a PM tool, you can also set notifications to track the progress.
- . Implement a Content Workflow
Best if you document the content work from ideation phase to optimization, review, approval and publishing so that your content follows the same guidelines and your brand tone of voice.
Conclusion:
Now that you have tackled the content part, you can move onto planning how you are going to promote your content. If you follow the guidelines above, the process of SEO content creation will be broken down into manageable, clear tasks and workflows. It will be easy for you to follow them and allow you to focus on the quality of content instead of on managing the entire process.