Proper page markup can improve your site’s search engine rankings and its positions in search results. This is an important part of SEO work that requires skills and understanding of how different types of markup function.
When a user makes a query, the search engine provides a list of relevant sites – the search results. Each item in this list is a search snippet – condensed information about the page.
The snippet influences the likelihood of a click – it either prompts the user to visit your site or to look at other links. The position in the search results primarily affects the likelihood of a click, but within 2-3 positions in the top-10, users make their choice based on the snippet.
Favicon
This icon can help if it is recognizable – for example, if it features a well-known brand logo. The favicon depends 100% on the Publisher. A free service that works without a VPN, like realfavicongenerator.net, can quickly create a favicon for any browser. It also checks how your site’s icons are currently displayed and whether they might be displayed incorrectly under certain OS or browsers.
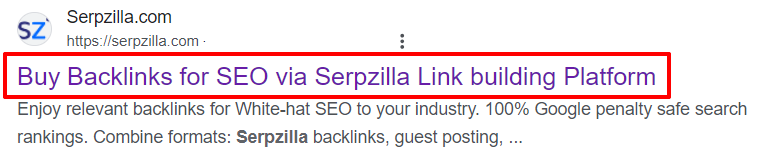
Page Title
- In most cases, the title is formed from the content of the title tag, although it can also pull from h1. To ensure the title tag is used, write unique titles that don’t duplicate those on other pages and don’t repeat h1. For e-commerce sites with hundreds of pages, a title generation service or Excel can help.
- Include the most frequent query promoted on the page in the title. The closer it is to the beginning of the title, the better. Pay attention to the number of characters. In Google, titles up to 65 characters are displayed without truncation
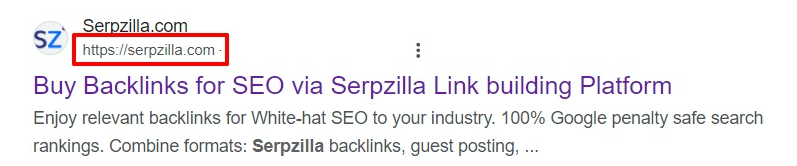
Page Link
The link will be displayed exactly as it is, so the Publisher’s influence here is also nearly 100%. Long links will be truncated. A snippet with a human-readable URL collects 45% more clicks. To properly form a human-readable URL, use a transliteration service.
Page Description
Google mostly takes the snippet text from the meta tag description. Sometimes it takes text from the description, but more often from a relevant part of the content on the page. Typically, this is text that is located closer to the beginning of the page, unique, and contains keywords in a natural form.
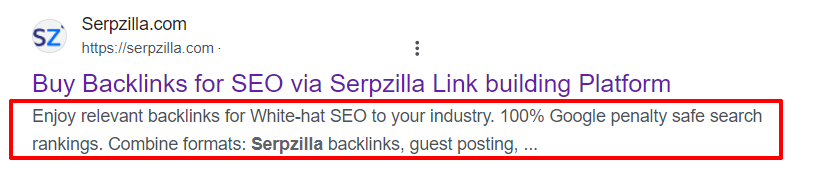
Marked Links
In the top-3 search results, Google may additionally display quick links. Schema.org is the most popular, free, and, in our assessment, the best service for microdata markup. It allows adding additional links, product ratings, prices, and other data.
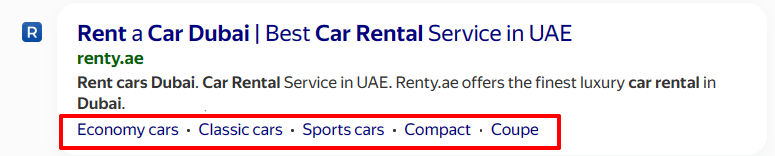
Optimizing Elements to Increase Traffic
In addition to the recommendations given in the previous section, here are a few more important tips:
1. Maximize the use of all tools you can influence.
Here’s an example of a snippet where the Publisher missed the opportunity to use the title and include important data in the description. Avoid this approach.

2. The closer the snippet is to the user’s query content, the better.
For commercial pages, it’s good to show the Unique Selling Proposition (USP) in the snippet. Or, at least, some essential information that is likely important to most users. A good example is profi.ru. At the very least, it immediately indicates the price, even in a “from” format.

3. Use numbers – they attract attention.
It’s hard to overdo it with numbers. When reading at the speed of scrolling – which is what we deal with in search results – it’s easier for the eye to catch numbers than text.
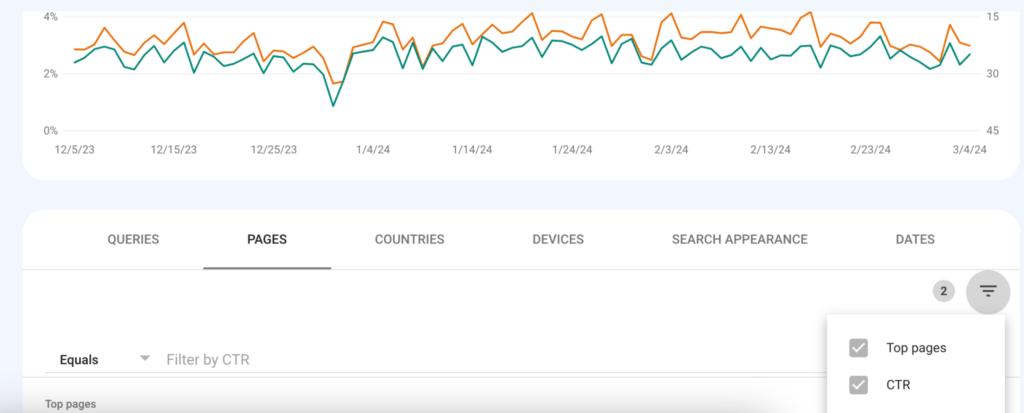
Finding Pages Where Snippets Need Work
Specifically, those already in the top-10 of search results but underperforming in traffic. Standard free tools like Google Search Console are used for this. Let’s look at an example using Google:
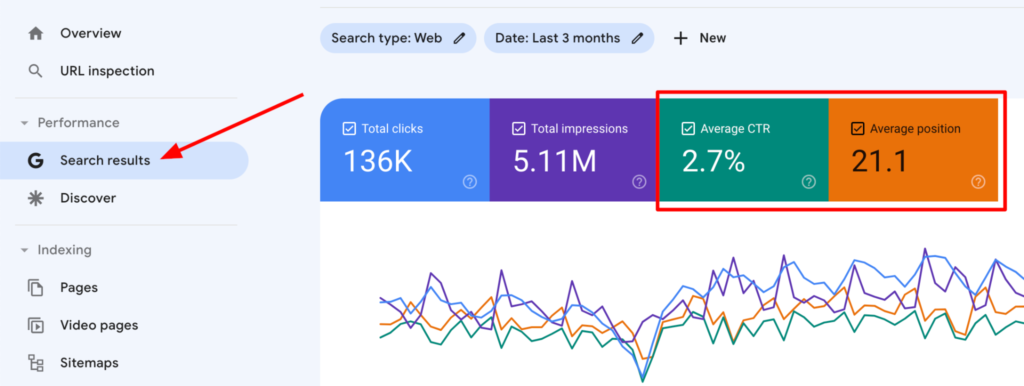
Step 1: Open the “Performance” report.
Step 2: Select the “Average CTR” and “Average Position” blocks.
Step 3: Choose pages that are close to the top of search results. If you are working with snippets for the first time, it’s optimal to experiment with pages in positions 6-8 in the top. On the one hand, they already gather some traffic, making this work worthwhile. On the other hand, if something goes wrong and the position drops, it’s regrettable but not as much as with pages in the top-5.
Step 4: Play with filters to highlight pages that receive less traffic than average for the site at a similar position.