To timely detect and resolve issues affecting site indexing, consider performing a series of checks.
Domain Name
Ensure that the site has a domain name. For example, such a problem arises when resources created on WordPress are set up incorrectly.
Users might be redirected to your site from an IP address instead of a domain name, or the IP address redirect is set up incorrectly. Try adding 301 redirects from www-versions of pages to redirect users back to the corresponding domain.
If you have more than one domain variant — especially in the case of a move from http:// to https:// — they need to be added to the console. It’s important not to miss any variations and to confirm your ownership of them. Otherwise, pages or the entire site might not be indexed in Google, as search engine robots will see a mismatch. However, this issue usually arises only with sites that have been around for a significant time.
Plugins and JavaScript
Some plugins on your site may be hindering page indexing. For example, the WordPress plugin Virtual Robots.txt, which is set to no robots, will completely block robots’ access to your resource.
Check your robots.txt and ensure it does not contain the line:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
The symbol “/” means that all pages in the root directory are closed to robots. The Disallow: line should not have any characters after the colon if you do not want to block specific site elements from indexing.
JavaScript can also hinder search engine robots. This can happen if the script is used to load content from users’ browsers. Moreover, it is not recommended to hide JavaScript and CSS files, as Google views these elements as needing to be accessible.
Noindex and Nofollow Meta Tags
Sometimes meta tags get the Noindex and Nofollow properties. For example, your site may link to a page that was indexed by Google robots and then deleted before the tags were properly set. As a result, the page may never be indexed again.
To avoid such situations, change the tags to index and follow. The larger the number of pages on the site, the more complex the process of manually checking and changing tags, but it is necessary work to protect your resource from frustrating errors.
Technical Optimization
Technical optimization is extremely important, and if you are not confident in your abilities, it is best to turn to professionals. Both users and search engines will appreciate the result.
Through technical optimization, you can fix a range of serious errors that can lead to pages being excluded from indexing:
- The site may not meet the standards of Core Web Vitals (a group of new ranking factors) relied upon by Google;
- Typos may be present in the code;
- Some pages may have a circular redirect, redirecting back to themselves;
- Site settings block the operation of search engine robots.
Loading Speed
Low loading speed is one of the factors why search engines lower a resource’s positions in search results. It affects a range of behavioral factors – increasing bounce rates and reducing time spent on the site.
Speed usually drops due to an abundance of content and its insufficient optimization. An old server with limited capabilities might also be used. If you encounter this problem, try the following solutions:
- Google PageSpeed Insights shows which pages need speed improvement. It checks whether it’s possible to reduce the number of connections, the load, browser caching, and other important parameters, and suggests ways to improve these aspects.
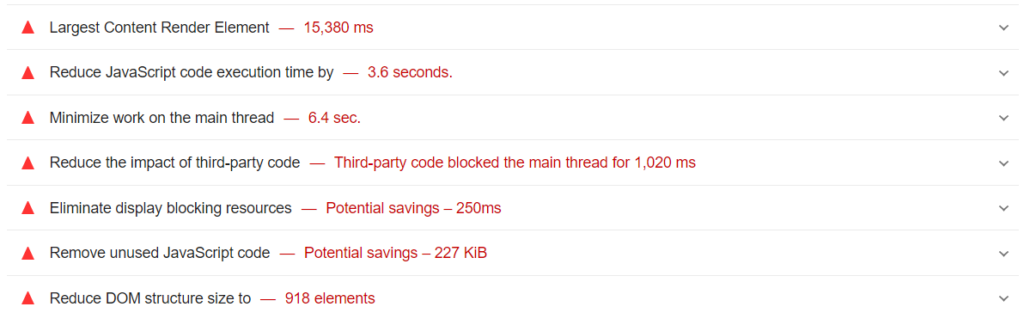
2. Use Webpagetest.org to assess the overall loading speed of the site. It also indicates which specific elements cause loading problems.
Sitemap
If you don’t use a sitemap, robots will inspect your site almost blindly. As a result, some pages may not get indexed. A Sitemap file will help indicate which pages are most important and should be regularly checked by the search engine. It’s better to create this file in XML format; using HTML format is not advisable.
Site Usability
The easier it is for users to navigate your site, the higher it will rank in search engine results. If a page loads too slowly, has complex navigation, or is cluttered with distracting apps, it may not get indexed.
Also, if you create pages for product categories, but each contains only one product, search robots may deem such pages unworthy of attention.
Implement interlinking so that users, delving deeper into the content, can always quickly and conveniently return back. Strive to give your audience the best possible experience on each page of your site.
Mobile Version
Your site must have a functional and adapted mobile version; otherwise, it is unlikely to be indexed. Content, links, or other optimization methods won’t help. If the content cannot be fully viewed from a tablet or smartphone, you will lose positions and traffic.
Insufficient optimization – text cannot be seen in its entirety without horizontal scroll
Mobile optimization is not complicated – just add adaptive design elements, such as flexible grids and media queries in CSS. This will already allow users to avoid navigation difficulties.
Quality of Text
Without well-written textual content, it is extremely difficult to even make it to the top 50, except in cases where the site is a gallery without any text. Aim for texts to be around 1,000 words. Texts shorter or longer than this are generally less informative – either they lack sufficient data, or there is an excess of “fluff.”
Content should answer users’ main questions or offer a qualitatively different perspective than other niche sites. Strive to maintain relevance and timeliness at the highest possible level.
Problems often arise with pages that have less than 100 words, regardless of the density of key queries. Search engines may consider them to be low-information and not index them.
Absence of Search Engine Penalties
If your site’s pages are not being indexed, it’s quite likely that you have been penalized, and you have not taken steps to correct the error. You may not even be aware that the pages are under sanctions and are banned from indexing.
More about sanctions, their diagnosis, methods of protection, and ways to get out of them are discussed in the “Sanctions” section.



