Search engines do not welcome all actions by site owners. Sometimes, if they go against the search engine’s policy, penalties in the form of penalties may follow. Search engine penalties vary in severity; for example, part of the site or the entire site may be excluded from search results.
Types of Google penalties
A search engine may consider a page unuseful for users in terms of content but at the same time over-spammed with keywords, and as a result, stop indexing it. Positions in search results will significantly drop, and traffic volume will decrease, which in turn can lead to additional deterioration in the site’s ranking.
In certain situations, a site can be completely banned. It is removed entirely from search results. Penalties of this level lead to the loss of all organic traffic from the search engine. A ban leads to the site’s quality level being reset, which adversely affects not only promotion but also, for example, monetization of the resource through selling links or placing media advertising.
Reasons Why Google Penalises your Website
Your website may be subject to Google penalties in the following cases:
- The site owner abuses the placement of non-original content;
- The site uses someone else’s content and is involved in affiliate programs;
- The site features auto-generated content (e.g., synonymized text);
- The site uses hidden redirects, content, or links;
- Using doorway pages with poor quality content, redirecting users to other pages;
- Incorrect use of microdata;
- Use of key phrases that do not match the theme and content of the pages;
- The site contains pages infected with viruses or offers malicious software for download.
Checklist: How To Identify a Google Penalty
There are several ways to determine if your website is under search engine penalties.
Brand Query Check
This method is recommended before purchasing a domain to avoid buying a “pig in a poke”. In Google search you need to enter the address of the site you are interested in. However, instead of a dot, put a space (for example, to check Serpzilla.com, the query would look like serpzilla com). A fully functioning domain should appear at the top of the search results. If this does not happen, the resource is likely banned by the search engine.
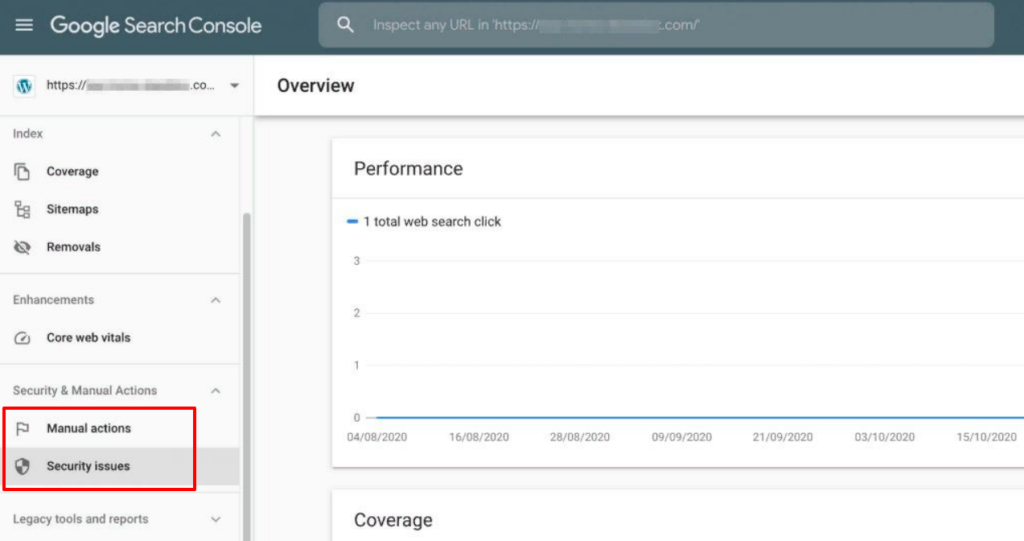
To find out how many pages of a website have been indexed in Google, enter the query site: site.com (replace site.com with the name of the site you’re interested in) on the search page. If the search does not register any pages, the site is excluded from the search results. If the number of indexed pages has noticeably decreased, it may indicate some error impeding indexing or the presence of a penalty filter.
Check Using Google Search Console (GSC)
The GSC service has a convenient check option that allows you to immediately establish the fact that the site has been blocked by the search engine. Go to the “Manual Actions” section – it displays messages about the resource being blocked.
Traffic Analysis
If you notice a sharp decrease in traffic to your site, especially if it has fallen to zero, the cause may be a filter imposed by a search engine or complete exclusion from search results. Check the Robots.txt file – make sure that all necessary pages of the site are available for indexing. The website might have been inaccessible for visits, or some work might have been carried out during the traffic drop period. Also, rule out hosting shutdowns and other technical reasons.
If the traffic drop period coincides with updates to search engine algorithms, then you may have been penalized because of them. Keep track of such updates to avoid this situation catching you by surprise.
Trust Level and Quality Check
Use various services, such as Ahrefs, to check the site’s trust indicator. If the quality parameter has dropped to zero, it’s a sure sign that the site is under penalties, up to complete blocking.
Checking with Specialized Tools
One of the simplest ways to detect the imposition of penalties is to use services that specialize in this. These include Panguin Tool, Google Penalty Checker, Website Penalty Indicator, PR-CY, and Xtool. Typically, each of these tools is designed to work only with one of the search engines, so to get complete information, you will need to use several such services.
How to Recover From a Google Penalty
After you have ruled out all possible errors and are finally convinced that your site is under the filters of search engines, identify the cause and try to eliminate it as quickly as possible. Remember that you always can contact Google technical support. This can be extremely useful if you can’t find out what exactly led to the imposition of penalties. Perhaps the domain you purchased was already under a filter, and you didn’t know about it.
When contacting technical support, you should clearly state your position and express your willingness to clarify the situation and make efforts to correct it. In this case, the official representatives of the search engine will meet you halfway and, if you actually eliminate the reasons that led to the penalties, will remove them from the site. There may be a situation where you disagree with the actions of the search engine administration – then the site owner has the right to file an appeal, thoroughly arguing their disagreement.
Typically, corrective actions will include significant content rework. If pages were spammed with keywords or contained useless, especially non-original, content, all problematic elements will need to be replaced.
Even in the best case, it will take some time for the filters or ban to be lifted. Moreover, the positions you lost in search results will likely have to be restored over a long period, and there is no guarantee that you will be able to do so fully. Be prepared for the fact that promotion may need to start on another domain, and this may require significantly less effort.



