Search engine positioning has become a focal point for many SEO experts. But Google’s ranking algorithms are constantly being refined, making them a challenge to keep up with.
Another relatively new phenomenon is AI Overviews (AIOs). Since they were introduced by Google in their present shape in May 2024, they have created quite a disturbance in the SEO world. More and more people rely on the AI summary and, as a result, won’t follow the links even on the first search result page.
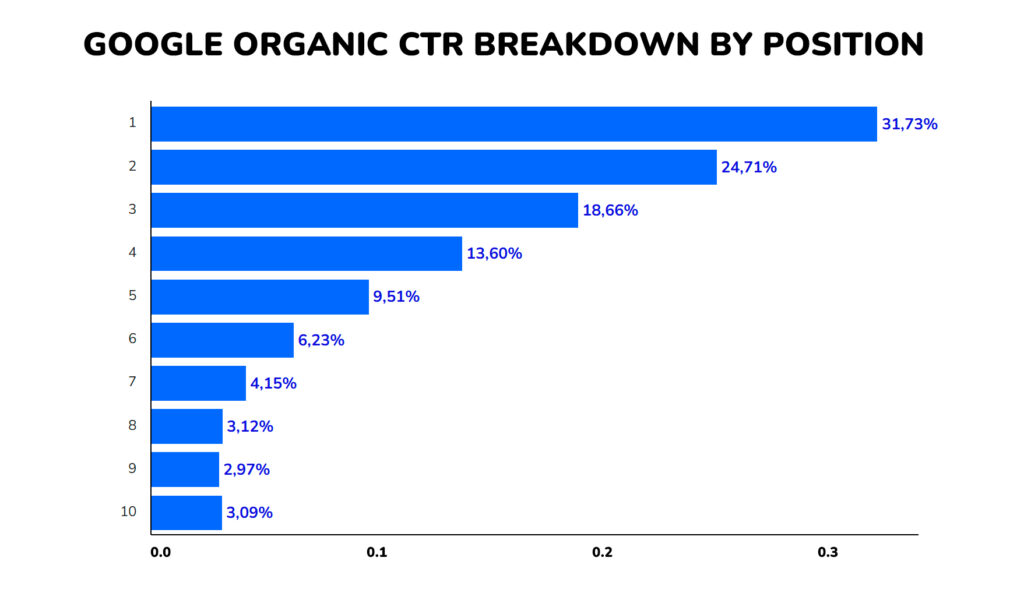
This affects mainly informational searches, which constitute up to 80% of all search traffic.
All this fuels increasing competition for visibility. Today, if you want to climb to the SERP top, traditional SEO tactics simply aren’t enough. So, in this guide, we’ll talk about what search engine positioning is, how it differs from general SEO, and which steps you can take to rank higher.
What Is Search Engine Positioning?
Search engine positioning refers to the specific ranking of your website’s individual pages for particular search queries and keywords on search engines like Google.
When someone types something related to your website’s subject into Google’s search bar, your website can appear in different places on the search results page—or not at all. You can influence how close to the top it is by making certain improvements to your content and SEO strategy.
A solid search engine positioning strategy can help you achieve high visibility and make your content easily discoverable. Ideally, your search engine positioning strategy should take you to the first SERP page for keywords that are most relevant for your business goals and content.
Another great placement is Google Featured Snippets or AI overview. While they take answers to user queries from your content, they also list sources. If a user wants details and not just a dry summary, they are highly likely to click on the source link.
👉 Example:
If you run an online store selling eco-friendly shoes made of natural but not animal-sourced materials, you’re good if you rank in the top 3 results for the keyword “vegan running shoes” in your target geo market.
The goal of search engine positioning is clear: continuously achieve high visibility for high-intent queries that drive organic traffic and conversions.
Another Example from Serpzilla: A food & wine business in Vietnam leveraged strategic link-building to grow its traffic five times. This directly demonstrates the power of effective positioning in driving real business growth.
Search Engine Positioning vs. SEO: What’s the Difference?
If you have been involved in SEO even for a little while, you probably already know that very often these two terms are used interchangeably. And yet, there is a distinct difference.
SEO is the general discipline—a science of improving your website’s visibility and organic search results. It comes with its own set of practices and strategies. Search engine positioning, on the other hand, is the outcome or result of those SEO efforts—it’s the specific place your page holds on the SERP for a particular search combination.
| Aspect | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | Search Engine Positioning |
| Nature | The process of optimizing a website for search engines | The result or outcome of SEO efforts (the rank/placement) |
| Focus | Broad website health and visibility across all queries | Specific ranking of individual pages for target keywords |
| Scope | Site-wide (architecture, UX, backlinks, etc.) | Keyword- and page-level refinement |
| Goal | Build long-term authority, crawlability, trust | Achieve high ranking for specific search terms |
| Strategy Type | Ongoing technical, content, and link-building efforts | Continuous tracking and fine-tuning per keyword/page |
| Example Actions | Improve Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, backlink profile | Adjust meta title for target keyword, optimize anchor text |
| Metrics | Organic traffic, keyword rankings (as a means), site speed, backlinks | Actual SERP rank, position changes, market share in search results |
👉 Tip: Think of SEO as the foundation, and positioning as the fine-tuning that helps your key pages win top spots.
Understanding Google’s Ranking System
Google employs a very complex set of interdependent factors to assign positions in search results. Some would even say that the system is convoluted. Each of these factors has a certain weight in rank calculation. This priority distribution is a subject of constant change and refinement, and Google is notorious for algorithm updates that upheave the SEO world.
One clear direction Google’s ranking system seems to be taking is getting better at discerning the user’s ultimate goal behind searches. Does the person searching for something want to learn, to buy, or to find a location? Many experts agree that Search Intent Matching is a top ranking factor in 2025.
Over the recent years, we have also been observing this: ranking algorithms shifted significantly from a keyword-centric approach to a more user-centric one. Today, to rank high in SERPs, you need to prioritize user experience and authentic quality content, moving beyond superficial optimization tactics.
Let’s break down Google’s ranking system in simple terms:
✅ Crawl & Index: Google’s bots discover and index your page.
✅ Analyze Relevance: Google evaluates your page’s content to see if it matches a user’s query (search intent).
✅ Evaluate Authority: Google checks signals like backlinks and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
✅ Assess UX & Performance: Page speed, mobile usability, and Core Web Vitals impact rankings.
✅ Adjust for Context: Personalization, location, and device type can alter the displayed position for different users.
👉 How is it connected to SERP positioning? Ultimately, your SERP position is the result of how well these elements fit into Google’s understanding of relevance, quality, and user satisfaction.
Key Factors That Influence Search Engine Positioning
What works best to improve search engine positioning today? There is no simple answer. But we can say that you need a holistic, user-centric approach that adapts quickly to different search behaviors. Let’s break down the core factor clusters:
Content Optimization
- Create high-quality, original, and credible content that demonstrates E-E-A-T.
E-E-A-T Component Key Strategies for Demonstration
| E-E-A-T Component | Key Strategies for Demonstration | Examples |
| Experience (E) | Share your personal experiences & case studies; Incorporate original research & data; Use rich media to document experience; Use user-generated content (UGC) strategically. | Behind-the-scenes content, industry surveys, process photos, customer testimonials. |
| Expertise (E) | Develop comprehensive, in-depth content; Display relevant credentials; Cite authoritative sources; Demonstrate technical knowledge. | Detailed author bios, professional certifications, linking to professional profiles, explaining complex ideas clearly. |
| Authoritativeness (A) | Earn quality backlinks from relevant sites; Get mentions from industry leaders; Demonstrate active industry presence; Build brand recognition. | Guest posting, industry awards, features in major publications (e.g., Forbes), consistent brand messaging |
| Trustworthiness (T) | Implement technical trust signals (HTTPS, speed, mobile responsiveness, structured data); Provide transparent information; Maintain current information; Manage online reputation. | SSL certificates, clear contact pages, prompt error corrections, responding to reviews, comprehensive “About Us” pages. |
- Match search intent: Deliver exactly what users seek, whether that’s information, products, or services.
Yes, keywords remain necessary for search engines to understand a page’s topic. For Google, however, it’s no longer about simple lexical matching. Semantic understanding plays a more important role in search engine positioning now.
Content that fails to align with user intent, even if technically optimized for keywords, will likely result in poor engagement metrics (high bounce rates, low dwell times). Ultimately, this will level down your SEO efforts. The weight of search intent matching is increasing because it directly correlates with user satisfaction—Google’s ultimate goal.
- Optimize for Google’s AI Overview: Make your content AI-friendly.
If you want your content to get picked up by AI Overview, it needs to “speak” in clear, unambiguous terms. Simple, concise language and structured formatting (e.g. headings, lists, FAQs) will make your content easy for AI to analyze and summarize. If you take your time to highlight authoritative information, answer questions directly, and include schema markup, your chances of being cited increase.
- Update regularly: Google favors fresh, up-to-date information.
This is especially important if your business domain deals with dynamically developing topics.
Optimizing for this aspect involves posting relevant, fresh content on a regular basis but also revisiting old content to introduce updates. Focus on evergreen content to make its shelf life longer.
📌 Example:
In January 2025, a digital PR and SEO blog published an article titled “Top 5 New SEO Strategies for 2025”, highlighting trends like AI Overviews and GEO.
- Throughout the year, the content team added timely posts:
- “How Google’s April Algorithm Update Affects SEO”
- “The Impact of AI Overviews on Organic Visibility”
- “How Google’s April Algorithm Update Affects SEO”
- Result: Google recognized the website as active and up-to-date in a dynamic niche.
Updating Evergreen Content
- Mid-year, the team updated the original Top 5 article:
- Replaced outdated tips
- Added insights on E-E-A-T and Core Web Vitals
- Included a “Last updated” label for credibility
- Replaced outdated tips
- The team maintained evergreen guides like:
- “How to Build High-Quality Backlinks”
- “Understanding Search Intent”
- “How to Build High-Quality Backlinks”
- Regular minor updates (stats, examples) keep content fresh and ranking strong.
- ~10% month-over-month organic growth is observed as a result.
User Experience
- Improve Core Web Vitals: Fast loading (LCP < 2.5s), quick interaction (INP < 200ms), stable layout (CLS < 0.1).
| Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Benchmark | Why It Matters for SEO |
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Loading speed – how long it takes for the largest visible element to load | Under 2.5 seconds | A slow LCP signals poor load performance and can lead to higher bounce rates. |
| INP (Interaction to Next Paint) | Responsiveness – how quickly the page reacts to user input (clicks, taps, etc.) | Under 200 ms | Replaced FID in 2025. Poor INP means laggy interaction, harming UX and rankings. |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Visual stability – how much page elements shift around during load | Under 0.1 | Unexpected shifts annoy users and lower engagement; Google penalizes unstable layouts. |
- Design for mobile first: Mobile usability is the primary factor for indexing and ranking.
- Make navigation intuitive: Reduce bounce rates and increase dwell time.
Technical SEO
- Secure your site: HTTPS is a basic ranking requirement.
An SSL certificate is usually a standard requirement for SEO and user trust in 2025.
- Ensure fast loading speeds: Optimize images, use CDNs, compress code.
- Use structured data: Help Google parse your content better and with more clarity.
Backlinks
- Quality over quantity always. It’s been proven by hundreds of SEO cases: a few strategically placed high-quality backlinks pass more link juice than dozens of random low-quality ones.
- Use tools like Serpzilla to create highly relevant pools of potential referring domains for your specific niche and SEO goal. Our smart filter algorithms will help you find link placement prospects that are just right for you.
📌 How Serpzilla Helps:
When you buy backlinks, two things need to be kept in mind: each purchase has to be safe and each link needs to have a positive impact. Serpzilla connects you with relevant and trusted websites that are legitimate and safe as referring domains.
This minimizes the risk of being slapped with a Google penalty. We at Serpzilla work hard to make sure you can get backlinks that Google views as positive endorsements of your content’s value.
Serpzilla constantly updates its extensive database of websites so that we can provide contextual and niche-relevant placements.
- Prioritize relevance: There has to be a logical, evident connection between a referring domain and your site. It has to be clear to a reader of your referring domain page why they are linking to you. Ideally, it has to be clear from the get-go. Thus, contextual placement, anchor text, and value need to be seen and understood immediately.
📌 Backlink Quality Checklist
✅ From high-authority domains
✅ Relevant to your niche
✅ Natural anchor text
✅ Placed editorially and naturally within text (not spammy)
✅ Brings referral traffic
Pro Tip: Serpzilla provides 40 key metrics, including geolocation, language, industry, spam score, domain rating, and traffic, to help you easily evaluate potential backlinks before making a purchase.
Make sure you research this information before you purchase.
It is also vital that you continue checking backlink health after the purchase through Serpzilla’s dashboard. There are multiple factors at work that can change backlink performance, so you need to monitor it.
How to Improve Your Search Engine Positioning: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Audit Your Current Positioning
- Use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to see where your pages rank.
- Select a number of target keywords where you’re sure you have the ability to improve performance (e.g., pages sitting at positions 5–15, with an adequate keyword difficulty level).
📌 Example: Use Ahrefs SERP Checker to see SERP results from any location
Practical Tip: Use your sales team’s insights. What questions do customers frequently ask? What are their objections? This direct feedback can inform content that addresses user needs at every stage of the funnel
Step 2: Optimize for Search Intent
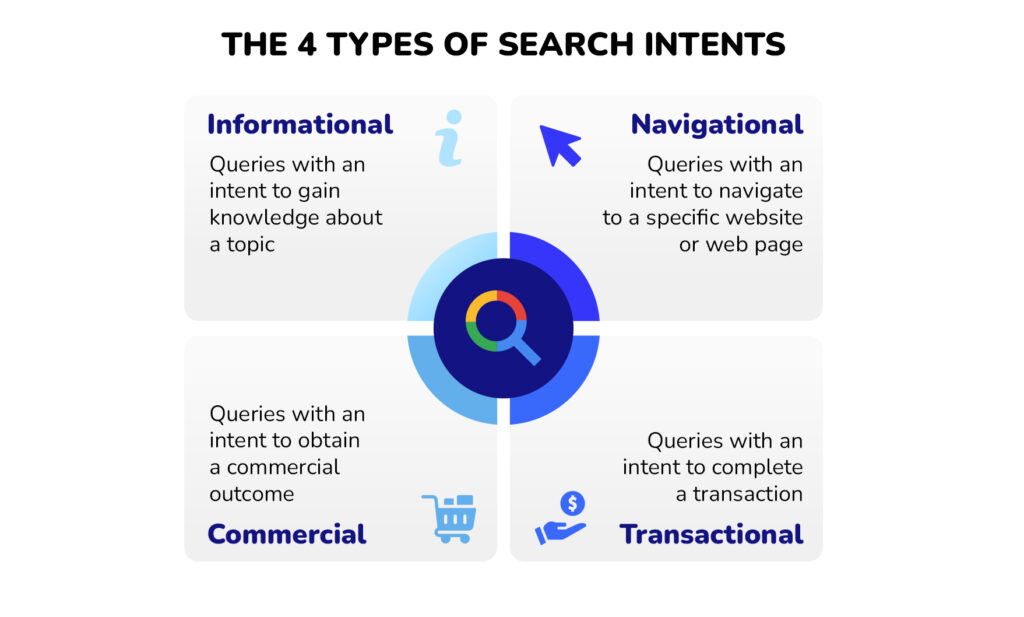
- Study your top-ranking competitors’ content and find out what is it that they offer that you don’t that you don’t (format, depth, media).
- Adjust your content to match the user’s intent fully. Sometimes you need a quick answer, at other times, it should be a tutorial or in-depth guide.
📌 Example: For a query like “best running shoes,” try to understand what it is that your user wants. Is it reviews (informational), a comparison (commercial investigation), or places to buy (transactional)? Depending on this understanding, choose your content’s format, depth, and tone.
Step 3: Strengthen Technical SEO & UX
✅ Technical SEO Website Optimization Checklist
- Check for and resolve duplicate content
- Optimize the robots.txt file
- Improve page loading speed
- Develop a user-friendly site architecture
- Implement structured data & schema markup
- Improve navigation with breadcrumbs
- Enable HTTPS to secure the site
- Optimize the XML sitemap
- Make sure the site is mobile-friendly
- Identify and fix crawl errors
- Optimize Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, FID)
Practical Tip: Regular audits of your site using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report are a great way to identify and fix performance bottlenecks.
Step 4: Build & Manage Backlinks with Serpzilla
- Use Serpzilla to identify high-authority, relevant sites offering link opportunities.
- When you insert a backlink, it has to be editorial and natural-looking: use the variety of link placement formats Serpzilla offers. You can do niche edits, link insertions, guest posts, and much more. You can fine-tune each link placement to make it look natural and maximize its value.
- Use Serpzilla’s smart filters to ensure safe placements that won’t trigger Google penalties.
Serpzilla offers unique expert tips on how to maximize its link-building features’ value:
How to Start a Link Building Campaign on a Budget
7 Effective Link Building Strategies for 2025
Serpzilla’s Guest Posting Tips and Guides
Step 5: Use AI-Driven Optimization (GEO)
- Implement Structured Data (Schema Markup): Explicit semantic context is what makes your content AI-friendly. Machine-readable content which you tweak for AI algorithms increases the likelihood of your pages landing citation links in AIOs. This improves your brand recognition even in zero-click searches.
- Optimize for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Focus on clear, concise, factual, and authoritative content that AI can easily extract and cite.
Practical Tip: For your domain, do some research on which content is being pulled into AIOs. Then you’ll be able to adapt your content structure. Best practices here include providing direct answers and key information clearly and concisely at the beginning of your articles.
Step 6: Focus on Conversion-Oriented SEO
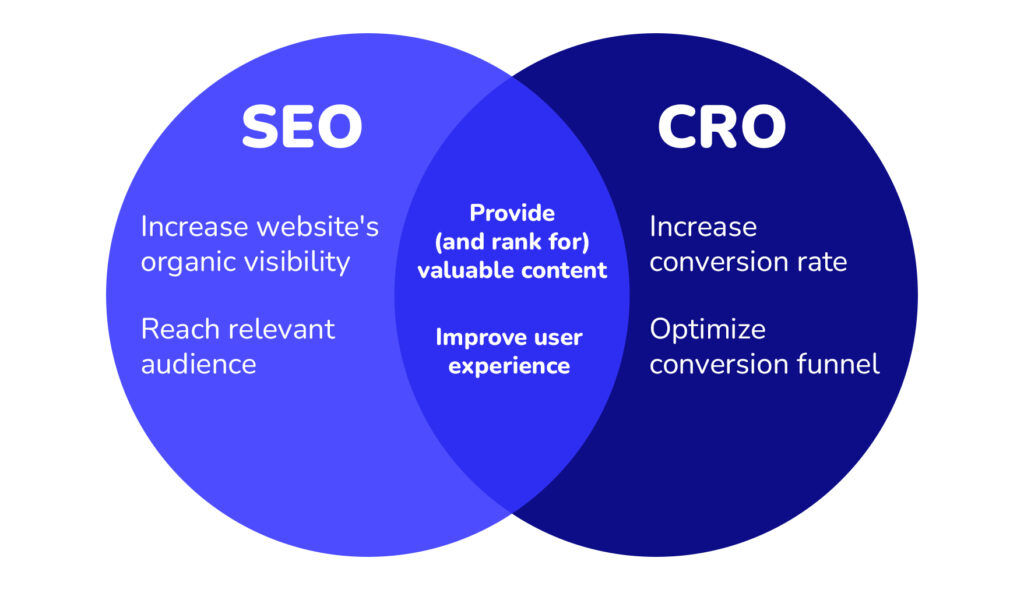
- Mid- and bottom-of-the-funnel content is key here. This is the kind of content that addresses purchase intent, answers specific product questions, and works with objections.
- Weave in “a-ha” moments of your product or service into informational articles using videos, GIFs, and demos to guide users towards conversion.
Practical Tip: Your sales and marketing teams could be invaluable sources of information for this. You need to understand the customer journey beyond the initial search. They found you, what do they do next? What will they want to know? Is this content readily available?
Then you can optimize your content to support decision-making at every stage. Measure SEO success by conversion rates, lead generation, and ROI, not just traffic volume.
How to Track and Evaluate Your Search Engine Positioning
| Metric | Why It Matters | Recommended Tools |
| Keyword position | Direct measure of search positioning | Google Search Console, Ahrefs |
| CTR | Shows if titles/meta descriptions attract | Google Search Console |
| Dwell time/bounce rate | Indicates content usefulness | Google Analytics |
| Core Web Vitals | Reflects UX quality | PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse |
| Backlink profile | Tracks authority signals | Ahrefs, Serpzilla |
👉 Tip: Set up monthly tracking dashboards to monitor progress and refine tactics.
Common Mistakes That Hurt Search Engine Positioning
Your SEO Disregards Search Intent
✅ You shouldn’t optimize for keywords out of context. Always ask yourself exactly what it is your user is searching for. There has to be a 100% match between your content creation goal and user search intent.
❌ Example: If, after optimization, a transactional query lands on your blog post instead of a product page, it’s bad SEO.
Irrelevant or Spammy Links
✅ Many link-building practices that were valid back in the day can be harmful today. We’re talking PBNs and random link batches.
✅ Use platforms like Serpzilla to vet link sources carefully.
❌ Spamming Reddit or Quora threads with links to your website can earn you an algorithm penalty.
Keyword Stuffing
✅ Make your backlink a natural part of your content. If it’s text, it should be an organic part of a sentence, yet illustrative of what users will find if they click on it.
✅ Focus on topic coverage and relevance rather than forcing in keywords.
❌ Over-optimization immediately flags your content as manipulative and reduces trust.
Final Thoughts
Search engine positioning in 2025 is as tricky and complicated as it gets. Chances are, it will get even more sophisticated in the future. However, if you employ a systematic approach and careful strategy – and rely on trusted tools such as Serpzilla – you can improve your SERP positioning. Follow actionable tips from this guide to stay ahead of Google’s algorithm updates and keep your SERP rankings high.