A link that leads to a non-existent page is called a broken link. Broken links can lead to the following negative consequences:
- Disappointed Visitors: Few things are as frustrating to users as a 404 error. It immediately reflects the negligence of the Publisher and causes irritation, especially when the sought-after information was of high importance.
- Reduced SEO Effectiveness: Internal links help search engine bots understand the structure of the site. If there are too many broken links on your site, it can significantly diminish the effect of all ongoing SEO efforts.
- Traffic Loss: In some cases, broken links can hinder the crawling of your site by search engine robots, resulting in a loss of positions in search results and valuable traffic.
Causes of Broken Links
There can be many reasons, but globally they fall into two categories: either the link was originally working but became broken over time, or it was broken from the beginning. In the first case, the reason could be on your side—if you have made any manipulations with the site, or on the side of the site that placed a link to you:
- URL Change: If you’ve changed the URL of a page, all links to this page will become broken. You need to update them so that they lead to the correct URL.
- URL Was Incorrectly Set at the Time of Link Placement: Common mistakes include adding spaces or extra characters to the link address, as well as confusion between http and https.
Therefore, when setting links, it’s crucial to ensure that the address is specified accurately. This problem is easier to prevent than to fix later. If the page to which the link led was deleted or never existed, then the link will also be broken. Sometimes links are created in advance for a planned page, but there may be situations when this page is never created. In some cases, a page is deleted to be replaced by another, but the links are not updated.
Links to Content
Another common issue arises when a link leads not to a website page but to some type of content:
- Video/audio file
- Document
- Image
Such elements are often moved around the site without considering the potential consequences, resulting in broken links. Sometimes, these elements are completely removed from the site. Therefore, track all elements you link to and check their relevance after any changes on the site.
Plugins and Applications
Broken links can also arise due to incorrect functioning of plugins and other elements on the page. For example, you may have issues with contact forms, social media plugins, Java scripts, or CSS files (used for styling pages). These elements can become outdated, stop functioning properly, or conflict with each other or with the site’s code, leading to broken links.
When working with plugins and applications, it’s crucial to regularly update them and check their compatibility with other elements of your site. This will help avoid creating broken links and ensure smooth functioning of your website.
Broken Links Due to Plugins and Other Page Elements
Broken links can arise from the incorrect functioning of plugins and other elements on the page. For example, issues with contact forms, social media plugins, Java scripts, or CSS files (used for styling pages) can occur.
For instance, if a social media plugin is not working, users won’t be able to share your content. This can prevent them from linking to it. Sometimes, a link may include your site’s data or email address—if the contact form is malfunctioning, users won’t be able to do this. The connection between the functionality of plugins and the effectiveness of links might not be obvious, but it exists, so the aforementioned aspects need to be regularly checked.
Website Downtime
The most significant problem for links is the downtime or cessation of a website’s functionality. Often, it’s due to issues with hosting or the domain name—for example, if you forget to pay for them or if the provider stops servicing for some other reason. Not only does it significantly reduce the effectiveness of links, but it also leads to a major drop in traffic. It’s particularly bad if you don’t notice the downtime promptly and fail to address the issue in time.
Redirects
Conducting technical work in general is fraught with damaging links. If you’ve updated the site’s structure but haven’t set up redirects from old URLs to new ones, the links won’t work.
Ideally, use 301 redirects, as 302 redirects are temporary. 301 redirects properly inform search engines that a page has moved. According to Google’s recommendations, it’s better to leave a 301 redirect on a page for at least a year.
Finding Broken Links
Internal links can be checked manually by simply navigating through them. This is a very laborious task that takes a lot of time. You can use the “Inspect” tool in Google Chrome. Open “Console” and refresh the page to see all 404 errors.
You can also use the Google Search Console tool — the “Page Indexing” section.
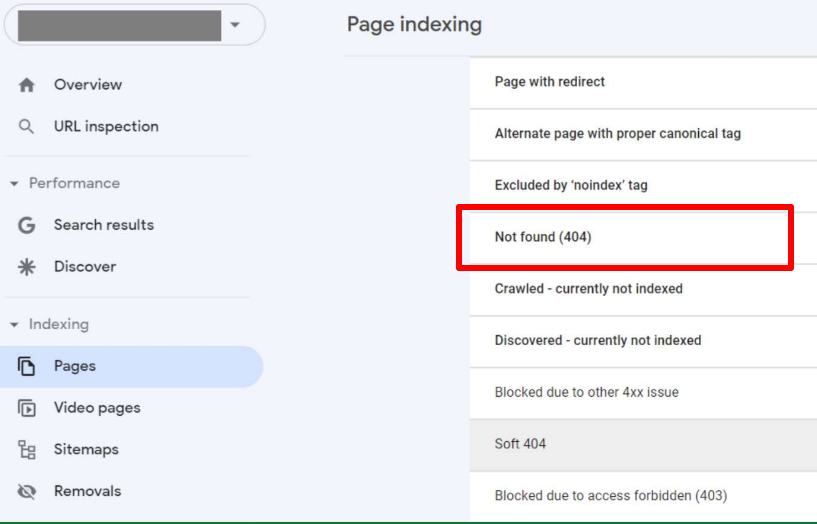
Another option is to download and install the Screaming Frog program. Simply enter your site’s URL and click Start. You can view the results in the program or download them as a CSV file.
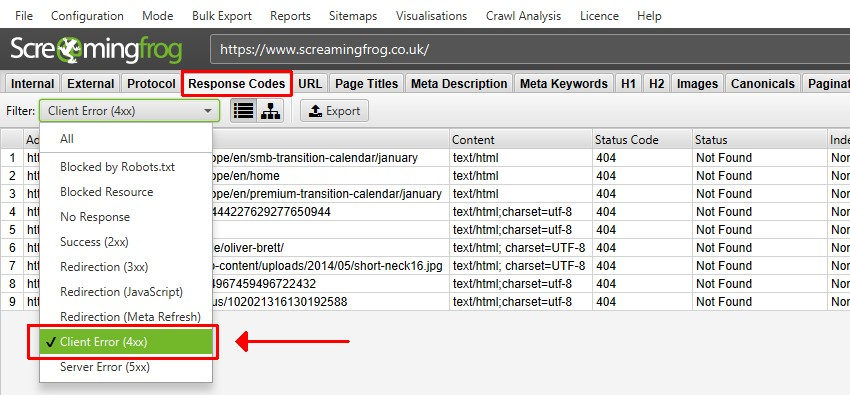
Choose the type of codes the program should find to detect 404 errors (example from ScreamingFrog.co.uk)
You can also search for broken links using Google Analytics by registering and going to the Traffic Sources > All Traffic > Channels > Organic Search section. It’s a good idea to check the site with this tool, then load the problematic pages into Screaming Frog to identify specific errors.
Fixing Broken Links
You can fix a broken link by redirecting it to a new page. In some cases, it might be better not to update the internal link, but to remove it. With Google Analytics, you can determine which pages receive more traffic and decide which links to fix and which to remove.
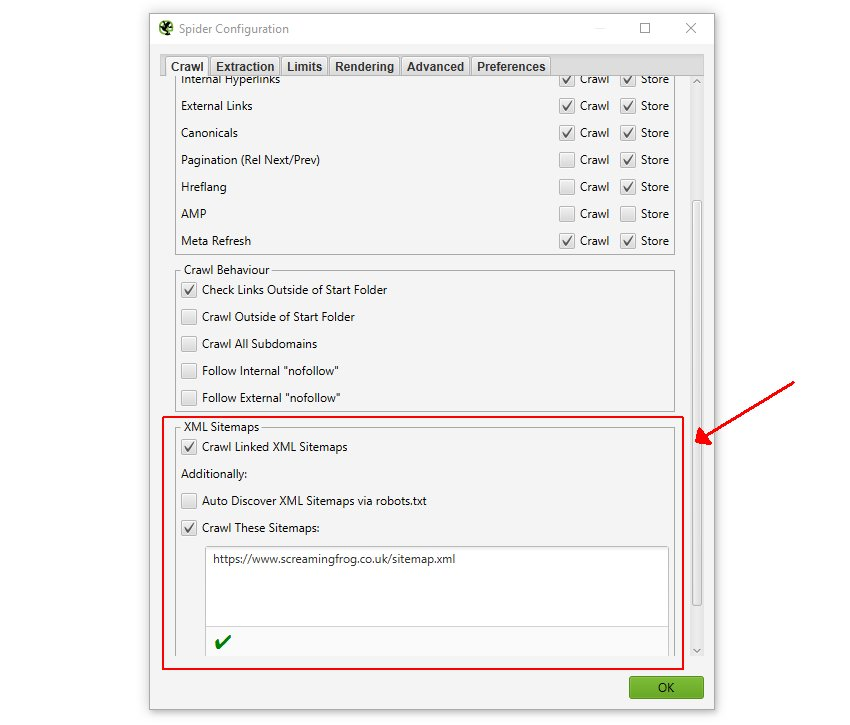
To simplify the fight against broken links, it’s strongly recommended to check the XML Sitemap. Download your site map and upload it to Screaming Frog. The program will detect the presence of broken links.
Search engine algorithms are designed so that users can find the information they need through a query. Consequently, if a search engine notices broken links on a site, it immediately considers it less effective for users than other resources and ranks it lower. In this case, the site loses positions and traffic, and the business loses clients and revenue.
The correctness of internal and external link building is critical not only for the site’s functionality but also for SEO. It’s necessary to continuously monitor the state of all links on the site — this point should be mandatory in your SEO-specialist’s checklist.



