Understanding search engine optimization is vital for successful website promotion. When generating search results for any query, search engines rely on their index of web pages. Knowing how indexing works, what facilitates it, and what hinders it is essential for successful website promotion.
Indexing is the foundation of search engine optimization. Search engines use special programs (search robots) to visit all the pages of all websites on the internet and add them to their index. It is from this index that Search Engines draw information when compiling search results.
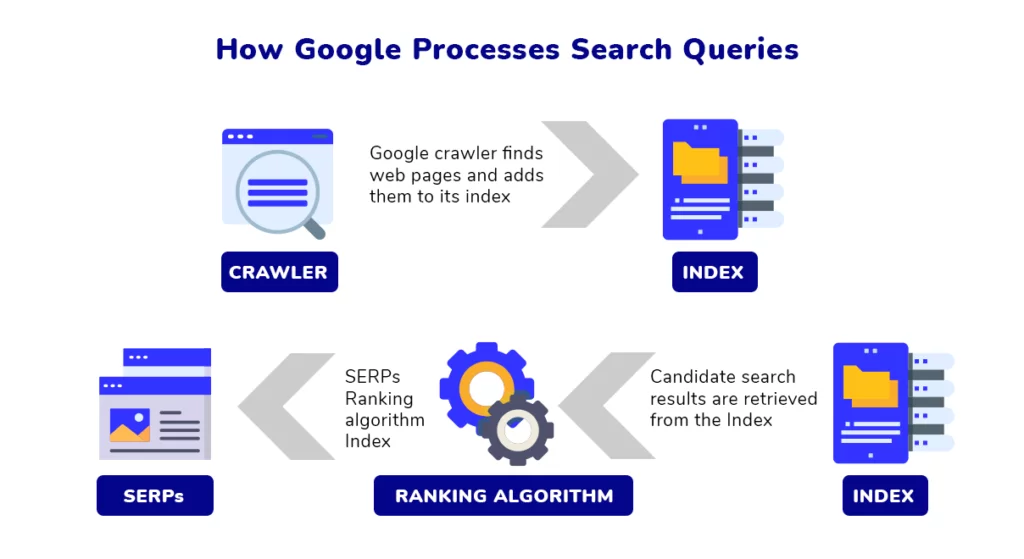
When a user submits a query, Search Engine algorithms determine what exactly the person wants to find and locate the most suitable pages in the index. The system then ranks the websites from most to least relevant, resulting in the search results.
Indexing a page takes time and can be done repeatedly. As the content of pages can change, Search Engines only learn about these changes after the next indexing. Changes won’t be considered until the updated version is included in the index.
If a site is not indexed, it means it’s not in the Search Engine’s database, and promotion efforts will be in vain. However, excessive indexing can be harmful, for example, if pages with duplicate content (pagination pages, filter pages, comments) are indexed.
Duplicates hinder promotion for several reasons:
- Such pages are often excluded from the index due to non-unique content.
- The search results might not display the page that is needed.
- Different pages might appear in the results each time.
- There is “cannibalization” of traffic – some documents will take traffic from others within the same site.
To avoid this problem, it is important to make site indexing:
- As accessible and convenient as possible for Google (create a sitemap, a robots.txt file, etc.).
- Correctly configured (so that the necessary pages of the site are available for indexing, while service and duplicate pages are closed or canonicalized).
- Protected during technical work or changes on the site (for example, improperly organized migration from HTTP to HTTPS often leads to pages disappearing from the index).



