Recent research by Axios and Graphite states that over 50% of content available on the internet in 2025 is completely AI-generated, or at least to some visible extent. And yet, according to the same research, only 12% of this content pops up in Google search results.
What happens with the rest? Is it Google penalizing it? Is there a simple lack of optimization? (It’s a known SEO fact that 96% of total pages online receive literally zero organic traffic from search engines).
Let’s try to answer this question in this article.
Why is the SEO community concerned with AI content evaluation by Google?
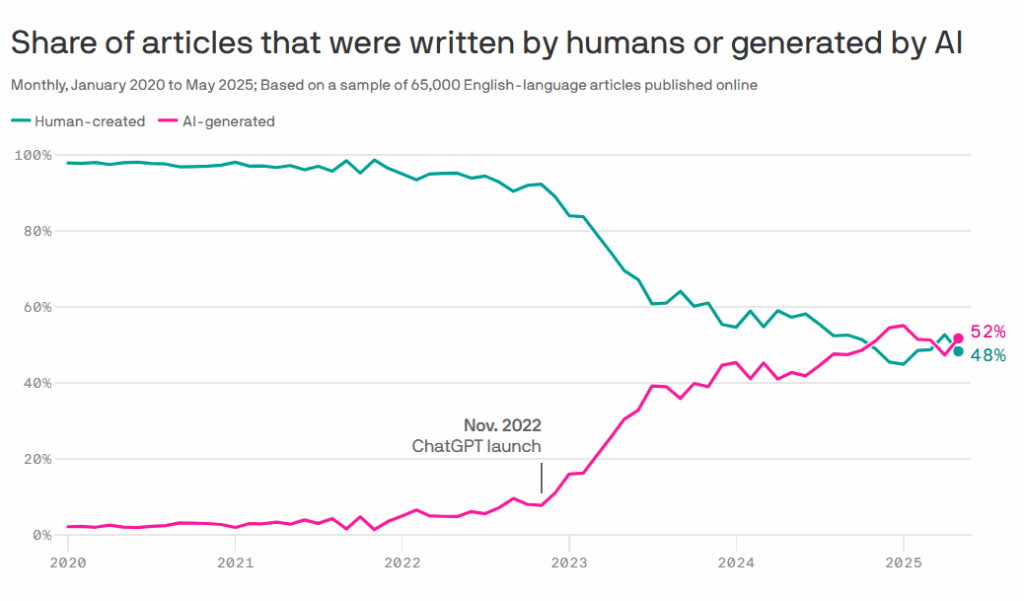
When OpenAI released ChatGPT in late 2022, it changed everything content-wise, from the way SEO professionals treat content to the way it is produced and scaled. Fast forward to 2025, and AI-generated text has become a cornerstone of modern content production. Agencies use it to scale guest posting, affiliate marketers rely on it for niche blogs, and even large publishers employ AI to generate drafts or data-heavy reports.
In less than three years, AI-generated or AI-assisted content overtook the entire World Wide Web. However, there are quite a few things AI hasn’t mastered yet (and may not master at all in the foreseeable future) — things like originality, creativity, and context nuances.
When surveyed about their attitude towards content that’s obviously AI-generated, most people react negatively. Various studies show that the majority of people are able to discern whether a text is AI or not from the first couple of paragraphs. The number is even higher for AI-generated images and videos.
And as soon as your content is labeled by viewers as “AI,”, it is usually greatly devalued, downgraded, and can even cause a backlash. Most major social media companies require users to tag AI-generated content, and if they don’t, they can get slapped with penalties.
It’s no wonder SEO professionals are concerned. Content is a foundation of SEO today, and if it’s viewed as worthless by users, search engines won’t be too far behind in giving it a negative assessment.
So, the big questions include: Does Google do it already? If yes, how does it detect AI content? And can AI still be used in content creation without risking a rankings drop?
Can Google detect AI content?
The answer to this question is more complicated than a simple yes or no. On the one hand, there are plenty of modern tools that have up to 99% accuracy when detecting AI, for example, SurferSEO’s AI detection tool. Other tools, like ZeroGPT, are also good for AI detection and are widely used by SEO professionals and content creators. However, they can have up to 10% of false-positive results, according to different estimations.
On the other hand, AI-assisted content, which is content partly generated by AI but edited by a human, is a grey area when it comes to detection.
Google doesn’t publicly disclose its detection methods, but several approaches are widely discussed and supported by case studies and patent filings:
- Statistical and Linguistic Analysis
AI text often shows recognizable statistical fingerprints like uniform sentence length, predictable n-gram frequency, and reduced lexical diversity. - Semantic Consistency and Fact Validation
Large language models occasionally produce “hallucinations” or inconsistent facts. Google’s Knowledge Graph and entity-based algorithms compare content statements against trusted databases to spot factual mismatches. - Pattern Recognition in Content Networks
When entire domains or networks publish similarly structured AI text (same patterns, syntax, or anchor usage), SpamBrain and other systems can mark it as manipulative. - User Interaction Metrics
Low engagement, short dwell time, and high bounce rates can indirectly suggest low content quality.
And what does Google itself have to say about it?
According to Google’s developers guide, the most important factor is not whether content is AI- or human-sourced, but whether it’s relevant, engaging, and whether it has value and is trustworthy. If E-E-A-T requirements are met, Google is apparently okay with it.
But surely it can’t be that simple? What about blog or commercial content?
Can Google Detect AI Content in Blog Posts or SEO Articles?
In 2025, Google’s ability to detect AI content depends less on the tool used (ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Jasper, etc.) and more on how the content is created and edited.
Several independent studies and experiments over the past two years have tested Google’s actual detection capabilities, and the results tell a сurious story.
🔬 Research and Independent Testing
- Originality.ai 2024 Detection Benchmark
In late 2024, Originality.ai ran a large-scale benchmark across 1,000 indexed articles written by both humans and AI.
- Result: Only about 67% of AI-written blog posts were correctly identified by AI detectors.
- However, when human editors revised AI drafts (adding data, examples, quotes, or personal experience), the detection rate dropped below 30%.
- This supports the idea that Google’s focus is on quality signals, not authorship.
- Result: Only about 67% of AI-written blog posts were correctly identified by AI detectors.
- SearchPilot SEO Experiment (2024)
A UK-based SEO testing platform, SearchPilot, published an experiment comparing traffic trends on AI-generated vs. human-written pages in similar blog categories.
- Finding: Google indexed and ranked both groups initially.
- After several months, pages with shallow, AI-generated text gradually lost visibility, while those edited and enriched by humans maintained stable or improved rankings.
- The decline correlated with low engagement metrics (short session duration, high bounce rate), suggesting user interaction and not AI detection triggered ranking adjustments.
- Finding: Google indexed and ranked both groups initially.
- SE Ranking / Ahrefs Case (2025)
Several SEO agencies reported that AI-assisted content optimized for EEAT — i.e., with author bios, citations, and firsthand examples — performed equally or even better than human-only content.
- For example, a SaaS company that replaced half of its blog pipeline with AI |& editor hybrid workflow saw a 12% increase in organic clicks over six months.
- This indicates that Google does not automatically demote AI text as long as it meets its Helpful Content standards.
- For example, a SaaS company that replaced half of its blog pipeline with AI |& editor hybrid workflow saw a 12% increase in organic clicks over six months.
⚙️ What These Findings Suggest
Google likely can detect the linguistic fingerprints of AI, especially when text is unedited, repetitive, or lacks semantic richness.
But in real-world SEO scenarios, what matters more are quality and authenticity signals:
- Does the content demonstrate real expertise or data?
- Does it answer the query better than competing pages?
- Do readers stay, engage, and share it?
When Does AI Content Lead to Manual Actions or Penalties?
Apparently, Google doesn’t penalize AI content just because AI was used in its creation. It penalizes content that violates its spam and quality guidelines, regardless of the source and authorship (human or machine).
However, in 2024–2025, multiple reports have shown that large-scale AI-generated sites have been deindexed or heavily down-ranked, often after algorithmic updates or manual actions triggered by low-quality or manipulative publishing patterns. But the key descriptors here are not “AI,” but “low-quality” and “manipulative.”.
Let’s look at how manual actions work, what recent cases revealed, and what common traits these penalized websites share.
What Is a Manual Action and How Does It Impact Websites?
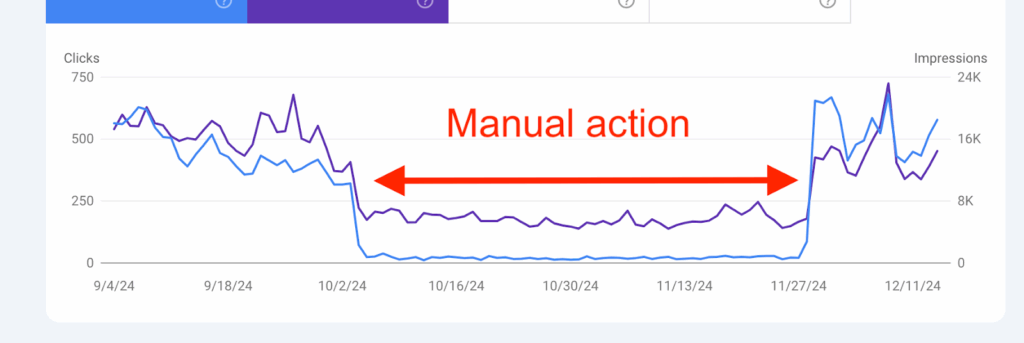
A Manual Action (or “manual penalty”) happens when a Google webspam reviewer manually inspects a website and determines that it violates Google’s Search Essentials. Typically, this is caused by spam, thin content, link manipulation, or malicious practices.
Manual actions can target:
- A specific URL or directory
- An entire domain
- A specific type of content (e.g., autogenerated articles, doorway pages, or scraped feeds)
When a site is hit:
- You’ll see a “Manual Actions” alert in Google Search Console (GSC) under the “Security & Manual Actions” tab
- The notification specifies the violation (e.g., “Pure Spam,” “Thin Content,” “Spammy Structured Markup”)
- Affected pages may be partially or fully removed from Google Search, resulting in a drastic traffic drop, often 80–100% overnight
What Did Recent Case Studies Reveal About AI Content Spam?
Between late 2023 and mid-2025, several large-scale experiments and incidents have confirmed that mass AI content production without editorial oversight can trigger penalties or deindexing.
🧪 Originality.ai Research (2024–2025)
Originality.ai tracked hundreds of AI-generated domains across niches like finance, travel, and entertainment.
- Finding: Sites with 90%+ unedited AI content experienced mass deindexing within 3–6 months of launch.
- In many cases, traffic dropped to zero overnight after the March 2024 Helpful Content Update.
- However, sites that combined AI drafts with human review, expert quotes, and structured data remained stable.
🧩 SpamBrain and the March 2024 Core Update
Google’s SpamBrain system, improved in the 2024 core update, can now detect patterns of low-value content networks, especially when entire domains publish hundreds of pages daily with similar syntax, tone, and zero backlinks from credible sources.
This led to mass removals of what SEO communities nicknamed “AI farm sites,” which were content hubs producing generic “Top 10” or “How To” articles with no unique insights.
What similarities exist across penalized websites?
Analysis across multiple reports (Originality.ai, Niche Site Project, SearchPilot, and Reddit SEO case studies) shows clear patterns among penalized domains.
| Common Trait | Description | Risk Level |
| Mass-published AI articles | Hundreds of new posts per day with repetitive structure, no editing | 🔴 High |
| No author info or EEAT signals | Missing bios, expertise proof, or external citations | 🔴 High |
| Keyword-stuffed or low-utility content | Content exists solely for ranking, not user value | 🔴 High |
| Homogeneous syntax and tone | Sentences of similar length and style, robotic phrasing | 🟠 Medium |
| Auto-generated internal links | Random linking patterns between AI posts | 🟠 Medium |
| No backlinks from real domains | Isolated in the web graph, indicating “content farm” structure | 🔴 High |
| Lack of user engagement | Low CTR, short dwell time, minimal comments/shares | 🟠 Medium |
Tools and Strategies to Detect & Improve AI Content Quality
If your SEO workflow already includes AI-assisted writing, the next logical step is quality assurance.
Before hitting “publish,” you should know how likely your content is to trigger spam signals and how to offset those risks.
Let’s look at tools that help evaluate AI-generated text and strategies to ensure Google sees your content as high-quality and helpful.
Which Tools Can Help Detect AI-Generated Content Before Publishing?
There’s a growing ecosystem of AI content detection tools. Some of them are built for SEO professionals and others for academic or editorial verification.
After testing those tools extensively, Serpzilla’s team can state that no detector is 100% accurate (especially after human editing).
What they are great at, however, is spotting red flags like repetitive syntax, wording regularly associated with AI (“in the fast-paced evolving world of SEO…”), and lack of connotations which makes your text too flat and robotic.
Below is a comparison of popular AI detection and quality-checking tools used by content teams in 2025:
| Tool | Primary Use | Detection Accuracy | Extra Features | Ideal For |
| Originality.ai | AI vs. Human content detection for SEO & agencies | ~85% on unedited AI content | Plagiarism scan, bulk site audit, API integration | Agencies, publishers managing multi-writer workflows |
| GPTZero | Academic-level detection focused on linguistic entropy | ~75% | Readability metrics, sentence-level analysis | Editors and educators |
| Writer.com AI Detector | Brand-focused AI and plagiarism detection | ~70% | Built into Writer’s content governance suite | Enterprise content teams |
| Content at Scale AI Detector | SEO-friendly detector analyzing “human probability score” | ~80% | Sentiment analysis, keyword density check | Bloggers, affiliate marketers |
| Copyleaks AI Content Detector | Multi-language AI detection | ~82% | Chrome extension, LMS integration | Multilingual SEO & content localization teams |
🧩 Pro Tip:
Don’t rely on a single tool. If SEO is largely driven by data, when it comes to AI detection, gut feeling is actually your best friend. If after reading a text it feels off, it’s better to trust that feeling. If it feels robotic to an editor who has a high level of exposure to such texts, chances are, it will feel unnatural to your readers as well.
How can Backlink Platforms Support AI-Driven SEO?
Even if your content is partly AI-generated, authority and trust signals can protect it from being devalued by Google’s quality algorithms.
One of the most effective ways to build that trust is through strategic backlinking, and this is where platforms like Serpzilla play a critical role.
Here’s how backlink platforms offset the risks of AI content:
- EEAT Signals
AI-generated content often lacks Experience and Trustworthiness. By placing links on authoritative, niche-relevant websites, you pass topical authority and trust signals to your domain. - Contextual Relevance
With Serpzilla’s Smart Topic AI and advanced filters, you can secure backlinks that are semantically aligned with your content. This contextual coherence helps Google’s algorithms interpret your page as authentic and relevant, not auto-generated spam. - Diversifying Link Sources
Many AI-heavy sites suffer because they exist in isolation. Serpzilla’s vast inventory — from niche blogs to reputable publishers — enables you to diversify your link profile, showing Google that your domain exists in a healthy, organic web ecosystem. - Guest Posts with Editorial Oversight
Serpzilla’s premium guest posting feature ensures human-edited, topic-relevant posts that combine AI efficiency with human credibility. - Faster Recovery from Algorithmic Drops
Case studies show that sites hit by content quality downgrades often regain visibility after rebuilding authority through targeted backlinks and brand mentions. Serpzilla’s platform allows this process to be data-driven and safe, without spammy link schemes.
Remember! Building trust and relevance with a smart backlink strategy will flop if your content is too obviously AI-generated, thin, unstructured, and irrelevant. Content quality comes first, and link building is a complementary measure.
FAQs
Does Google’s originality report in Google Docs detect AI content reliably?
No, Google’s originality report in Docs isn’t designed to detect AI. It identifies matching text from online sources and potential plagiarism, not whether content was generated by an LLM like ChatGPT or Gemini.
If you need to evaluate the AI-likelihood of your content, use specialized tools such as Originality.ai, Copyleaks, or GPTZer.
Can AI-generated pages rank if they’re edited and fact-checked?
Yes, and there’s abundant proof of that.
Pages created with AI assistance that are fact-checked, edited for clarity, and enriched with expert commentary or unique data consistently rank well.
For example, many publishers (including Bankrate, CNET, and niche SaaS blogs) continue to gain visibility with AI-assisted workflows because they follow Google’s guidance and prioritize useful, people-first content.
AI can accelerate drafting, but it’s human oversight that ultimately makes the content meet EEAT criteria.
Which warning signs suggest a penalty for AI content?
Typical red flags include:
- A sudden drop in organic traffic (50–100%) across large portions of the site.
- Pages disappearing from indexed results in Search Console several weeks after launch.
- A “Manual Actions” or “Pure Spam” alert appearing in GSC.
- Massive content churn — thousands of similar posts with low engagement.
If these occur, audit the site for low-quality automation and thin content. Replace or merge unhelpful pages, and request reconsideration once quality improves.
Should AI-assisted content always list a human author?
Yes — ideally.
Google’s EEAT framework rewards transparency and accountability. Listing a real human editor or subject-matter expert means that the information has been reviewed for accuracy and aligns with the Experience and Trustworthiness aspects of EEAT.
An attribution such as “Written with AI assistance, reviewed by [Author Name]” is perfectly acceptable and even encouraged in editorial contexts.
Does Google treat AI SEO tools differently from human writing?
No. Google has repeatedly confirmed that it doesn’t discriminate based on the tool, only on the output quality.
Using AI for keyword clustering, topic ideation, content outlines, or even first drafts is fine, provided the final result is helpful, accurate, and relevant.
Where penalties arise is when publishers use AI to mass-produce pages with no added value.
Is there a “safe percentage” of AI content in a site’s publishing mix?
There’s no official threshold, but evidence from 2024–2025 studies suggests that keeping AI-authored content under ~30% of total output, and ensuring it’s editorially reviewed, minimizes risk.
Websites that rely on 80–90% unedited AI content tend to experience volatility or deindexing.
Ultimately, success depends less on the percentage and more on editorial quality, backlinks, and user satisfaction, areas where tools like Serpzilla help maintain strong authority signals.